4 Signs You May Have Deep Vein Thrombosis -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a condition characterized by the formation of a blood clot, known as a thrombus, in one of the deep veins, usually in the legs. DVT can have serious implications if the blood clot dislodges and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
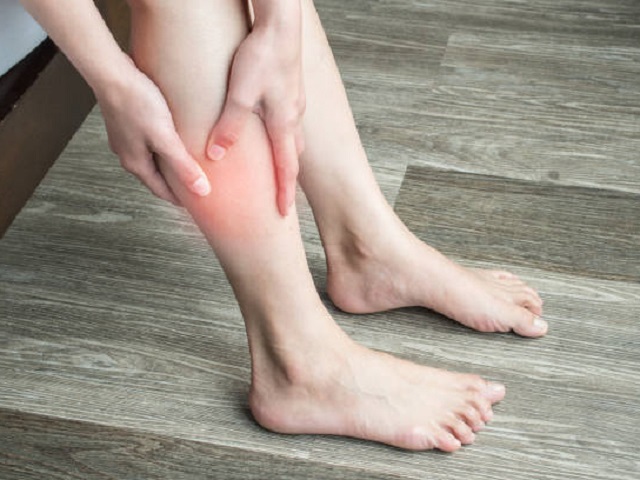
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
The symptoms of DVT can vary, but they may include:
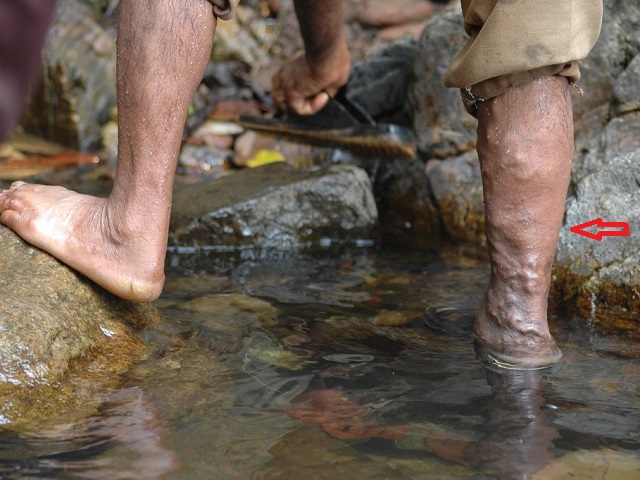
- Swelling in the affected leg, ankle, or foot.
- Pain or tenderness, often described as a cramp or a deep ache.
- Warmth and redness over the affected area.
- Skin discoloration, such as a bluish or reddish tone.
It's important to note that not everyone with DVT will experience noticeable symptoms, and sometimes the condition can be asymptomatic.
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
To diagnose DVT, healthcare providers may use the following approaches:
- Ultrasound imaging: This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of the veins and detect the presence of blood clots.
- D-dimer blood test: This test measures the levels of a substance called D-dimer, which is produced when a blood clot breaks down. Elevated D-dimer levels can indicate the presence of a blood clot, although further imaging tests are typically required for confirmation.
- Venography: In some cases, a contrast dye may be injected into a vein, followed by X-rays to visualize the blood flow and detect any blockages caused by blood clots.
Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis
DVT can occur when there is a combination of factors that disrupt the normal blood flow or increase the risk of blood clot formation. Common causes and risk factors include:
- Prolonged immobility: Long periods of immobility, such as during long-distance travel or bed rest, can increase the risk of DVT.
- Surgery or trauma: Certain surgeries, especially those involving the lower extremities or abdomen, can increase the risk of blood clot formation. Trauma or injury to the veins can also contribute to DVT.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as cancer, heart failure, inflammatory bowel disease, and inherited clotting disorders, can increase the risk of DVT.
- Hormonal factors: Hormonal changes, such as those associated with pregnancy, the use of oral contraceptives, or hormone replacement therapy, can increase the risk of blood clot formation.
- Age and obesity: Advancing age and obesity are risk factors for DVT.
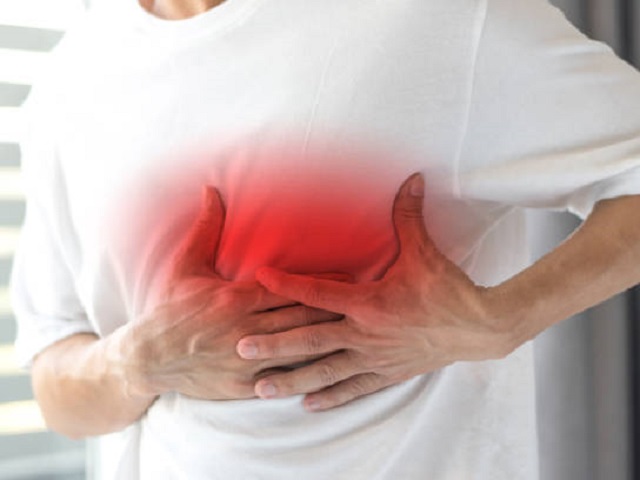
Effects of Deep Vein Thrombosis
If a blood clot in the deep veins dislodges and travels to the lungs, it can cause a potentially life-threatening condition called pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism occurs when the blood clot blocks the blood flow to the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing, chest pain, and even death in severe cases. Additionally, DVT can cause long-term complications, including chronic venous insufficiency and post-thrombotic syndrome, which can result in leg swelling, pain, and skin ulcers.
Treatment and Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis
The treatment and prevention of DVT typically involve:
- Anticoagulant medication: Blood thinners, such as heparin and warfarin, are commonly prescribed to prevent the clot from growing and to reduce the risk of further clot formation.
- Thrombolytic therapy: In certain cases, medications known as thrombolytics may be used to dissolve the blood clot more quickly.
- Compression stockings: Wearing compression stockings can help prevent swelling and promote blood flow in the legs.
- Inferior vena cava (IVC) filters: In rare cases where anticoagulant therapy is not possible, an IVC filter may be inserted into the vein to catch blood clots before they reach the lungs.
- Lifestyle changes: Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, avoiding prolonged periods of immobility, and quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of DVT.
It's essential to seek medical attention if you suspect you have symptoms of DVT or if you are at risk due to certain predisposing factors.
References:
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2020). What Is Deep Vein Thrombosis? Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/deep-vein-thrombosis
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Deep vein thrombosis (DVT). Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/deep-vein-thrombosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20352557
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019). Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)/Pulmonary Embolism (PE) - Blood Clot Forming in a Vein. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/spanish/dvt/index.html