4 Signs You May Have Genital herpes -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
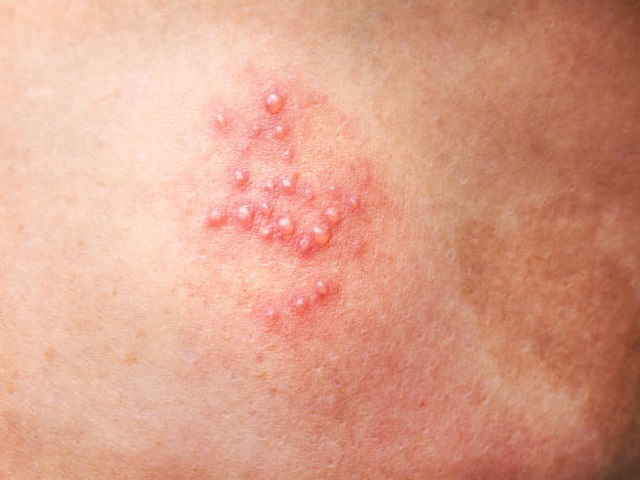
Genital herpes is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is primarily transmitted through sexual contact and can affect both men and women. Genital herpes is characterized by the presence of sores or blisters in the genital area.
Symptoms of Genital Herpes:
The symptoms of genital herpes can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience mild or no symptoms, while others may have more noticeable signs. Common symptoms include:
- Small, painful blisters or sores on or around the genitals, anus, or buttocks.
- Itching or tingling sensation in the affected area.
- Pain or discomfort during urination.
- Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, headache, and swollen lymph nodes.
Causes of Genital Herpes:
Genital herpes is primarily caused by the herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), although it can also be caused by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1), which is typically associated with oral herpes. The virus is usually transmitted through sexual contact with an infected person, including vaginal, anal, or oral sex. It can be transmitted even when no visible sores are present, as the virus can be shed through the skin.
Effects of Genital Herpes:
Genital herpes can have physical, emotional, and social effects on individuals. The recurrent outbreaks of sores can cause pain, discomfort, and inconvenience. Additionally, the stigma associated with genital herpes can impact relationships, self-esteem, and overall well-being.
Treatment and Prevention of Genital Herpes:
While there is no cure for genital herpes, antiviral medications can help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and duration of outbreaks. These medications can also reduce the risk of transmission to sexual partners. Prevention strategies for genital herpes include:
- Safe sex practices: Using latex condoms correctly and consistently during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of transmission, although it may not provide complete protection due to the potential for viral shedding outside of the covered areas.
- Testing and communication: Knowing your own and your partner's STI status and discussing it openly can help make informed decisions about sexual activity.
- Abstaining from sexual activity: Avoiding sexual contact is the most effective way to prevent the transmission of genital herpes.
It is important to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and guidance on prevention strategies for genital herpes.
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021). Genital herpes - CDC Fact Sheet. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/std/herpes/stdfact-herpes-detailed.htm