4 Signs You May Have Gout -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
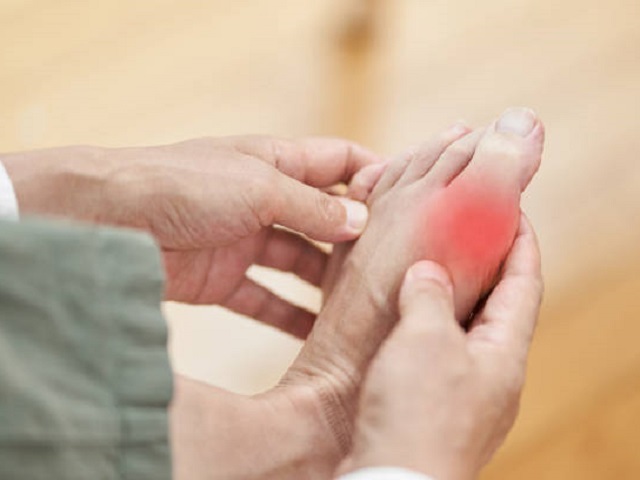
Gout is a type of inflammatory arthritis that causes sudden and severe joint pain, most commonly affecting the joint at the base of the big toe. It occurs due to the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, leading to inflammation and pain.
Symptoms of Gout
The symptoms of gout can include:
- Sudden and intense joint pain: Typically, the pain starts suddenly and often affects the joint at the base of the big toe, but it can also occur in other joints such as the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, or fingers.
- Swelling and redness: The affected joint may become swollen, tender, and red.
- Limited range of motion: Gout can cause a decreased range of motion in the affected joint.
- Warmth and stiffness: The joint may feel warm to the touch and become stiff.
Diagnosis of Gout
Diagnosis of gout involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The doctor may perform joint fluid analysis to check for the presence of uric acid crystals in the joint fluid. Blood tests may also be done to measure the level of uric acid in the blood.
Causes of Gout
Gout is caused by an accumulation of uric acid in the body. Factors that can contribute to the development of gout include:
- Elevated uric acid levels: Gout occurs when there is an excess of uric acid in the blood, which can be due to either overproduction or reduced excretion of uric acid by the kidneys.
- Diet: Consuming foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and sugary drinks, can increase uric acid levels and contribute to gout.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of developing gout.
- Family history: Gout can run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
Effects of Gout
If left untreated or poorly managed, gout can lead to complications such as:
- Recurrent gout attacks: Gout attacks can recur, causing repeated episodes of severe joint pain and inflammation.
- Joint damage: Over time, gout can cause damage to the joints, leading to chronic pain, joint deformities, and loss of mobility.
- Kidney stones: Uric acid crystals can also form kidney stones, which can cause severe pain and affect kidney function.
Treatment of Gout
Treatment options for gout may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids can help relieve pain and reduce inflammation during gout attacks. Long-term medications, such as xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosurics, may be prescribed to lower uric acid levels and prevent future gout attacks.
- Lifestyle changes: Making dietary modifications, such as reducing intake of purine-rich foods and alcohol, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying hydrated, can help manage gout.
- Rest and elevation: Resting the affected joint and elevating it can provide relief during gout attacks.
- Cold compress: Applying a cold compress to the affected joint can help reduce swelling and relieve pain.
Prevention of Gout
To prevent gout and reduce the frequency of gout attacks, the following measures may be helpful:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Losing weight if overweight and maintaining a healthy weight can help lower the risk of gout.
- Limit purine-rich foods: Avoid or limit consumption of foods high in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and sugary drinks.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water and fluids to help flush out uric acid from the body.
- Limit alcohol intake: Alcohol, especially beer, can increase the risk of gout. Limit alcohol consumption or avoid it altogether.
- Medication adherence: If prescribed medications to manage uric acid levels, it is important to take them as directed by the healthcare provider.
References:
Mayo Clinic. (2020). Gout. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gout/symptoms-causes/syc-20372897
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Gout. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/gout.html
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. (2019). Gout. Retrieved from https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/gout