4 Signs You May Have Ringworm -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Ringworm, also known as dermatophytosis, is a common fungal infection of the skin, scalp, or nails. Despite its name, it is not caused by worms but by a group of fungi called dermatophytes. Ringworm is highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct contact with an infected person, animal, or contaminated objects. While it can affect people of all ages, it is particularly common among children. Prompt treatment is essential to manage the infection and prevent its spread.
Symptoms of Ringworm:
The symptoms of ringworm vary depending on the area of the body affected. Common symptoms include:
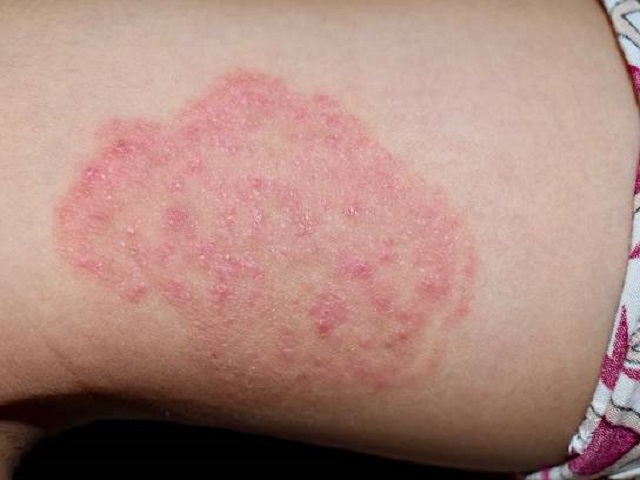
- Red, itchy, and scaly rash: The affected area typically appears as a red, circular or oval-shaped rash with raised edges and clear skin in the center.
- Itchy or painful skin: The rash may be itchy or cause discomfort and may become more severe over time.
- Hair loss: When ringworm affects the scalp, it can lead to hair loss in the affected area, resulting in bald patches.
- Brittle or discolored nails: Ringworm can affect the nails, causing them to become brittle, discolored, thickened, or crumbly.
Causes of Ringworm:
Ringworm is caused by various species of dermatophyte fungi, including Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. These fungi thrive in warm and humid environments and can be contracted through direct contact with an infected person or animal, or by sharing contaminated items such as towels, clothing, or sports equipment.
Effects of Ringworm:
If left untreated, ringworm can lead to complications and further spread of the infection. Scratching the affected area can cause secondary bacterial infections, and in some cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body or to other individuals.
Treatment and Prevention of Ringworm:
Treatment of ringworm typically involves the use of antifungal medications, which can be applied topically as creams, lotions, or powders, or taken orally in more severe cases. Over-the-counter antifungal creams may be sufficient for mild cases, while prescription-strength medications may be necessary for more severe or persistent infections.
Prevention strategies for ringworm include:
- Practicing good hygiene: Wash your hands regularly and thoroughly, especially after coming into contact with potentially contaminated surfaces or animals.
- Avoiding sharing personal items: Do not share towels, clothing, or other personal items with individuals who have ringworm.
- Keeping the skin clean and dry: Moisture can promote fungal growth, so it is important to keep the skin clean and dry, especially in areas prone to sweating.
- Avoiding contact with infected animals: If you have pets, ensure they receive regular veterinary care and treatment for any fungal infections.
- Maintaining a clean living environment: Regularly clean and disinfect common areas and objects, especially in communal spaces.
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Ringworm. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/fungal/diseases/ringworm/index.html
American Academy of Dermatology. (n.d.). Ringworm. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/ringworm-overview