6 Signs You May Have Psoriasis -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
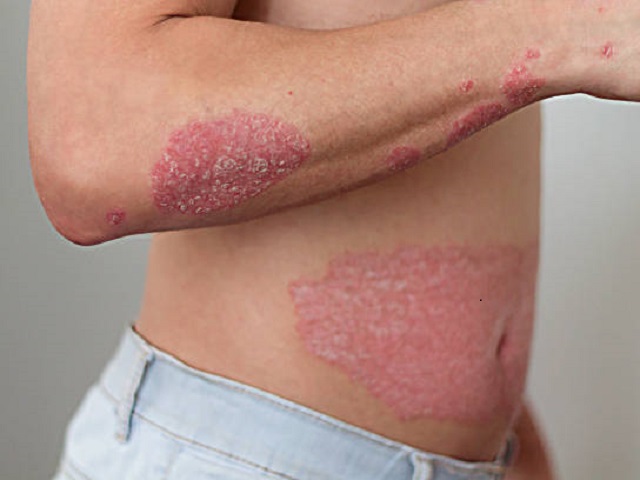
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that primarily affects the skin. It is characterized by the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. Psoriasis can occur on any part of the body and may be accompanied by other symptoms and complications.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Common symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Red, inflamed skin: Raised, red patches of skin covered with silvery scales.
- Itching and discomfort: Itching, burning, or soreness in the affected areas.
- Dry, cracked skin: Dryness and cracking of the skin, which may lead to bleeding.
- Nail changes: Pitting, thickening, or discoloration of the nails.
- Joint pain: Psoriatic arthritis, a form of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis, can cause joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
The diagnosis of psoriasis is usually made by a dermatologist based on the appearance of the skin and the presence of characteristic symptoms. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis by examining a small sample of affected skin under a microscope.
Causes of Psoriasis
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, immune system, and environmental factors. Possible causes and risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition: Certain genetic variations are associated with an increased risk of developing psoriasis.
- Immune system dysfunction: An abnormal immune response triggers inflammation and accelerates the skin cell growth cycle.
- Environmental triggers: Factors such as infections, stress, certain medications, and injury to the skin can trigger or worsen psoriasis in susceptible individuals.
Effects of Psoriasis
Psoriasis can have various effects on individuals, including:
- Physical discomfort: Itching, pain, and discomfort associated with psoriatic lesions can impact daily activities and quality of life.
- Emotional impact: Psoriasis can affect self-esteem, body image, and mental well-being, leading to feelings of embarrassment, frustration, and depression.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Up to 30% of people with psoriasis may develop psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, potentially leading to joint damage.
Treatment and Prevention of Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and control the disease:
- Topical treatments: Creams, ointments, and gels applied to the skin to reduce inflammation, alleviate itching, and promote skin healing.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light to slow the growth of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- Systemic medications: Oral or injected medications that modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation throughout the body.
- Biologic drugs: Targeted biologic therapies that specifically block certain immune system proteins involved in psoriasis.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including managing stress, avoiding triggers, moisturizing the skin, and quitting smoking, may help reduce symptoms and flare-ups.
Prevention of psoriasis is not currently possible, given its complex nature and genetic predisposition. However, avoiding known triggers, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and promptly treating any skin infections or injuries may help manage the condition.
References:
National Psoriasis Foundation. (n.d.). About Psoriasis. Retrieved from https://www.psoriasis.org/about-psoriasis
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Psoriasis. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/psoriasis/symptoms-causes/syc-20355840