7 Signs You May Have Interstitial Lung Disease -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Image by Patrick J. Lynch, medical illustrator, CC BY 2.5, via Wikimedia Commons
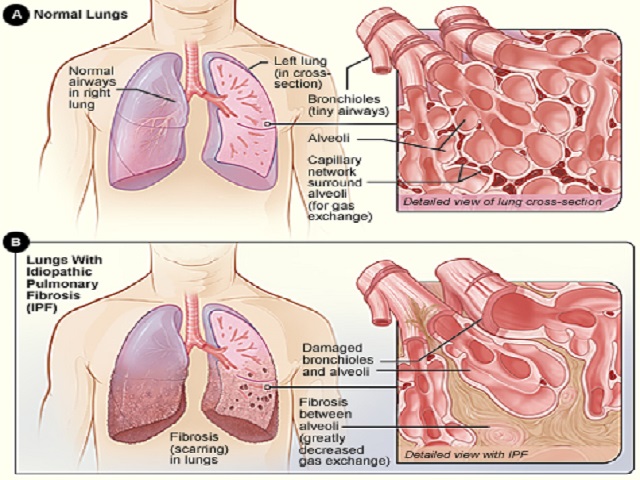
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) refers to a group of lung disorders characterized by inflammation and scarring of the lung tissue, specifically the interstitium, which is the space between the air sacs in the lungs. It can result in progressive lung damage and impaired breathing function.
Symptoms of Interstitial Lung Disease:
The symptoms of ILD may vary depending on the specific type and stage of the disease, but common symptoms may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Dry cough that may persist over time
- Fatigue and weakness
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Loss of appetite and unintended weight loss
- Clubbing of fingers (widening and rounding of the fingertips)
- Bluish coloration of the lips or skin (in advanced stages)
Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Disease:
The diagnosis of ILD typically involves the following:
- Medical history and physical examination: The doctor will inquire about symptoms, medical history, and exposure to potential risk factors.
- Pulmonary function tests: These tests measure lung capacity and function, including spirometry, lung volume measurement, and diffusing capacity tests.
- Imaging tests: High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scan of the chest helps visualize the lung tissue and detect abnormalities.
- Bronchoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube with a camera into the airways to evaluate the lung tissue and collect samples for analysis.
- Lung biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of lung tissue may be obtained for further examination under a microscope.
Causes of Interstitial Lung Disease:
The causes of ILD can be categorized into several groups, including:
- Occupational and environmental exposures (such as asbestos, silica dust, or certain chemicals)
- Connective tissue diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic sclerosis)
- Drug-induced ILD (caused by certain medications)
- Idiopathic (unknown cause), as in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)
- Infections, such as pneumonia or tuberculosis
Effects of Interstitial Lung Disease:
ILD can lead to significant effects on the lungs and overall health, including:
- Progressive scarring and fibrosis of the lung tissue
- Reduced lung capacity and impaired oxygen exchange
- Difficulty in breathing, especially with physical exertion
- Increased susceptibility to respiratory infections
- Pulmonary hypertension (high blood pressure in the lungs)
- Reduced quality of life and functional limitations
Treatment of Interstitial Lung Disease:
The treatment of ILD focuses on managing symptoms, slowing disease progression, and improving overall lung function. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and other medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and slow the progression of the disease.
- Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen may be provided to improve oxygen levels in the blood and relieve symptoms.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: This program includes exercises, breathing techniques, and education to improve lung function and enhance daily functioning.
- Lung transplantation: In advanced cases, lung transplantation may be considered for eligible candidates.
Prevention of Interstitial Lung Disease:
Prevention strategies for ILD include:
- Minimizing exposure to occupational and environmental lung irritants
- Using protective measures, such as masks or respirators, in work environments with potential respiratory hazards
- Early diagnosis and treatment of underlying conditions, such as connective tissue diseases
- Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke
- Regular monitoring of lung health and seeking medical attention for respiratory symptoms
It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment options, and ongoing management of interstitial lung disease.
References:
Raghu, G., et al. (2018). An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 198(5), e44-e68. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST