8 Signs You May Have Cardiomyopathy -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Cardiomyopathy refers to a group of diseases that affect the heart muscle, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively. There are different types of cardiomyopathy, including dilated cardiomyopathy, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and restrictive cardiomyopathy.
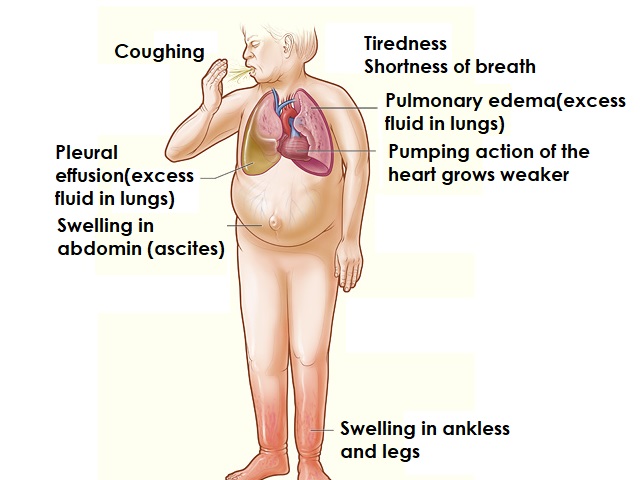
Symptoms of Cardiomyopathy
The symptoms of cardiomyopathy can vary depending on the type and stage of the disease. Common symptoms may include:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet (edema)
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting or near-fainting spells
- Diagnosis of Cardiomyopathy
To diagnose cardiomyopathy, healthcare professionals may perform several tests, including:
- Physical examination: The doctor will listen to the heart and lungs, check for signs of fluid retention, and evaluate overall health.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the electrical activity of the heart to detect any abnormalities in rhythm or structure.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test creates detailed images of the heart to assess its structure, function, and blood flow.
- Cardiac MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging provides detailed images of the heart, helping to evaluate its structure and function.
- Cardiac catheterization: In some cases, a catheter may be inserted into the heart to obtain more precise measurements of its function and blood flow.
Causes of Cardiomyopathy
The exact causes of cardiomyopathy may vary depending on the type. However, some common factors that contribute to its development include:
- Genetic factors: Inherited gene mutations can lead to the development of certain types of cardiomyopathy.
- High blood pressure: Uncontrolled hypertension can strain the heart muscle and lead to its weakening over time.
- Heart tissue damage: Heart attacks, infections, and other conditions that damage the heart muscle can result in cardiomyopathy.
- Alcohol and substance abuse: Excessive alcohol consumption or substance abuse can weaken the heart muscle and cause cardiomyopathy.
- Certain medications and toxins: Prolonged use of certain medications or exposure to toxic substances can contribute to the development of cardiomyopathy.
Effects of Cardiomyopathy
If left untreated or unmanaged, cardiomyopathy can have serious effects on heart function and overall health, including:
- Heart failure: Cardiomyopathy can lead to the progressive weakening of the heart muscle, impairing its ability to pump blood effectively and resulting in heart failure.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms can occur in individuals with cardiomyopathy, increasing the risk of complications such as blood clots and stroke.
- Sudden cardiac arrest: In some cases, cardiomyopathy can lead to sudden cardiac arrest, where the heart abruptly stops functioning.
Treatment and Prevention of Cardiomyopathy
The treatment and prevention strategies for cardiomyopathy depend on the type and severity of the condition. They may include:
- Medications: Certain medications, such as beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics, may be prescribed to manage symptoms, improve heart function, and prevent complications.
- Implantable devices: In advanced cases, devices such as pacemakers or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) may be implanted to regulate heart rhythm and prevent sudden cardiac arrest.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgical interventions like heart valve repair, heart transplant, or ventricular assist device (VAD) implantation may be necessary.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing stress, can help prevent or manage cardiomyopathy.
References:
American Heart Association. (2021). What Is Cardiomyopathy? Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/cardiomyopathy
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Cardiomyopathy. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cardiomyopathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20370709
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2021). Cardiomyopathy. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/cardiomyopathy
Cleveland Clinic. (2021). Cardiomyopathy. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17069-cardiomyopathy