8 Signs You May Have Pyelonephritis -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
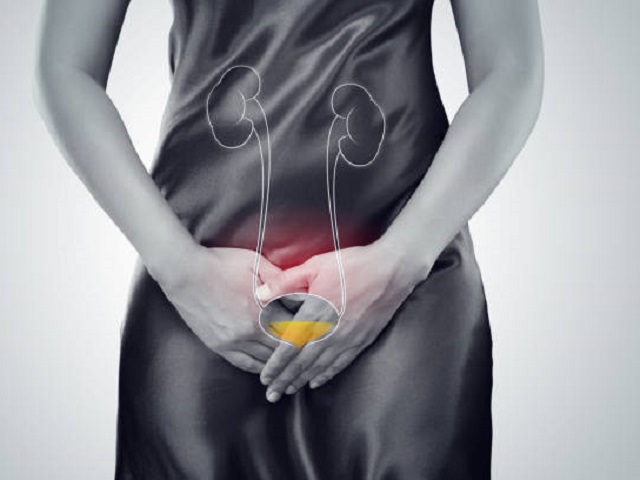
Pyelonephritis is a type of urinary tract infection (UTI) that involves the kidneys. It is characterized by inflammation and infection of the renal pelvis, which is the area where urine collects before it is excreted. Pyelonephritis can be either acute or chronic and is typically caused by bacteria entering the kidneys from the lower urinary tract. Here is an explanation of pyelonephritis, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Pyelonephritis:
The symptoms of pyelonephritis may vary, but common signs include:
- High fever with chills and sweating
- Flank pain or pain in the lower back or side
- Frequent, painful urination
- Urgency to urinate
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis of Pyelonephritis:
Diagnosing pyelonephritis involves the following assessments:
- Medical history and physical examination: Evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
- Urine analysis: Examination of a urine sample to detect the presence of bacteria, white blood cells, and other indicators of infection.
- Urine culture: A laboratory test to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic treatment.
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI may be used to visualize the kidneys and assess for any structural abnormalities.
Causes of Pyelonephritis:
The most common cause of pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection, usually stemming from a UTI. The bacteria typically responsible for pyelonephritis are Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally inhabit the intestines but can enter the urinary tract and ascend to the kidneys. Risk factors for developing pyelonephritis include:
- Urinary tract abnormalities or blockages
- Bladder dysfunction or incomplete bladder emptying
- Kidney stones
- Weakened immune system
- Use of urinary catheters
- Pregnancy
Effects of Pyelonephritis:
If left untreated or recurrent, pyelonephritis can lead to several complications, including:
- Kidney damage: Prolonged inflammation and infection can cause scarring and impair kidney function.
- Kidney abscess: Pus-filled pockets can form in the kidney, requiring drainage and antibiotic treatment.
- Sepsis: Severe infection can spread to the bloodstream, leading to a life-threatening condition called sepsis.
Treatment of Pyelonephritis:
Treatment of pyelonephritis typically involves:
- Antibiotic therapy: Oral or intravenous antibiotics are prescribed to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. The choice of antibiotic may depend on the severity of the infection and antibiotic resistance patterns.
- Adequate hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications may be used to alleviate discomfort.
- Hospitalization: Severe cases or individuals with complicating factors may require hospitalization for intravenous antibiotics and close monitoring.
Prevention of Pyelonephritis:
To reduce the risk of pyelonephritis, the following preventive measures may be taken:
- Drink plenty of fluids to maintain urinary tract health.
- Practice good hygiene, including regular handwashing and proper cleaning of the genital area.
- Urinate frequently and empty the bladder completely.
- Avoid holding urine for extended periods.
- Treat UTIs promptly and complete the full course of prescribed antibiotics.
- For individuals prone to recurrent UTIs, prophylactic antibiotic therapy or other preventive strategies may be recommended.
It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plan, and advice specific to individual circumstances.