9 Signs You May Have Arrhythmias -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Arrhythmias refer to abnormal heart rhythms or irregularities in the heart's electrical system. They can cause the heart to beat too fast (tachycardia), too slow (bradycardia), or with an irregular pattern. Arrhythmias occur due to various factors, including underlying heart conditions, electrical system abnormalities, or external triggers. They can range from harmless and temporary to serious and life-threatening. Here is an explanation of arrhythmias, along with their symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Arrhythmias:
The symptoms of arrhythmias can vary depending on the type and severity. Common symptoms include:
- Palpitations (sensations of a racing, fluttering, or irregular heartbeat)
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Fainting or near-fainting episodes (syncope)
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Sweating
- Anxiety
Diagnosis of Arrhythmias:
Diagnosing arrhythmias typically involves the following assessments:
- Medical history and physical examination: Evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and risk factors.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): A recording of the heart's electrical activity, which helps identify abnormal rhythms.
- Holter monitor: A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to record continuous ECG data and capture any intermittent arrhythmias.
- Event monitor: A portable device that can be worn for a longer period to record ECG when symptoms occur.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of the heart to assess its structure and function.
- Electrophysiological study (EPS): A procedure to study the heart's electrical system and provoke arrhythmias for diagnosis.
Causes of Arrhythmias:
Arrhythmias can have various causes, including:
- Heart conditions: Coronary artery disease, heart attacks, heart failure, valve disorders, congenital heart defects, and other structural abnormalities can disrupt the heart's electrical system.
- Electrical system abnormalities: Disruptions in the heart's electrical pathways, such as abnormal conduction pathways or malfunctioning nodes, can cause arrhythmias.
- High blood pressure
- Thyroid disorders
- Diabetes
- Substance abuse (such as excessive alcohol or drug use)
- Medications or other substances that affect heart rhythm
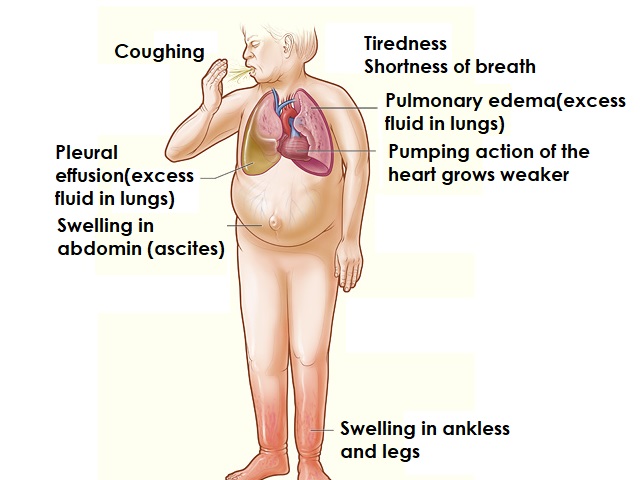
Effects of Arrhythmias:
Arrhythmias can have several effects on cardiovascular health, including:
- Reduced blood flow to vital organs
- Increased risk of blood clots, stroke, or heart failure
- Decreased cardiac output and compromised heart function
- Sudden cardiac arrest or other life-threatening complications
Treatment of Arrhythmias:
The treatment of arrhythmias aims to restore normal heart rhythm, manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications. Treatment options may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Avoiding triggers such as caffeine or alcohol, managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight, and regular exercise.
- Medications: Antiarrhythmic medications to control heart rhythm, blood thinners to reduce clotting risks, and other medications to manage underlying conditions.
- Cardioversion: Electrical cardioversion or medications to restore normal heart rhythm.
- Catheter ablation: A procedure to selectively destroy abnormal heart tissue responsible for arrhythmias.
- Implantable devices: Pacemakers to regulate heart rate or implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs) to correct life-threatening arrhythmias.
Prevention of Arrhythmias:
While not all arrhythmias can be prevented, certain measures can help reduce the risk:
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Adopt a balanced diet, exercise regularly, manage stress, and avoid smoking or excessive alcohol consumption.
- Manage underlying conditions: Control high blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
- Follow medication regimens: Take prescribed medications as directed, and inform healthcare professionals of any new symptoms or side effects.
It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plan, and advice specific to individual circumstances.
References:
American Heart Association. (2022). Arrhythmia. Retrieved from https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/arrhythmia
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Arrhythmia. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-arrhythmia/symptoms-causes/syc-20350668
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2020). Arrhythmia. Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/arrhythmia