Critical Signs You May Have Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
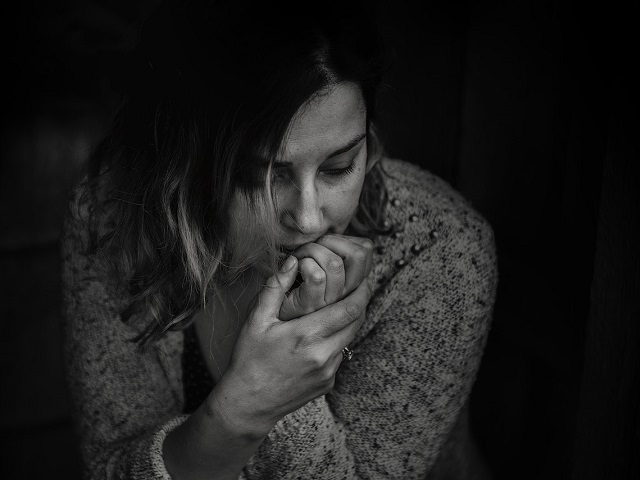
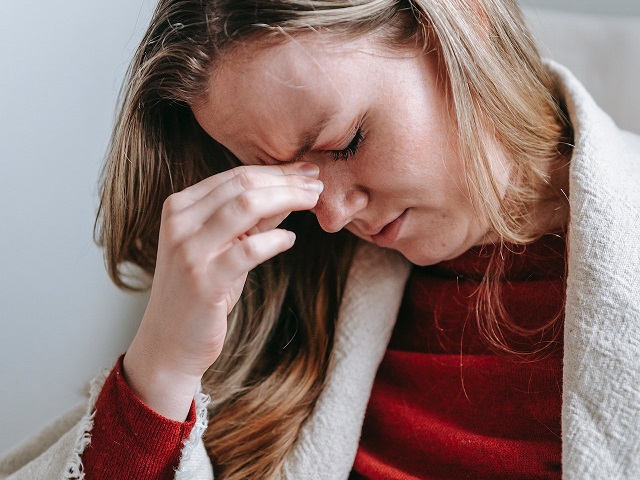
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition that can develop in individuals who have experienced or witnessed a traumatic event. It is characterized by a range of symptoms that persist beyond the traumatic experience and significantly impact daily functioning. Traumatic events may include natural disasters, accidents, physical or sexual assault, military combat, or other life-threatening situations. PTSD can affect people of all ages and backgrounds. Here is an explanation of post-traumatic stress disorder, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
The symptoms of PTSD can vary but generally fall into four categories:
Intrusive symptoms:
- Distressing memories, nightmares, or flashbacks of the traumatic event.
- Intense psychological distress when exposed to reminders of the trauma.
- Physical reactions, such as a rapid heartbeat or sweating, in response to triggers.
Avoidance symptoms:
- Avoiding places, people, or activities that remind the individual of the trauma.
- Efforts to avoid thoughts, feelings, or conversations associated with the traumatic event.
- Feelings of detachment, emotional numbness, or a sense of a limited future.
- Negative changes in cognition and mood:
- Negative thoughts or beliefs about oneself, others, or the world.
- Persistent negative emotional states, such as fear, anger, or guilt.
- Loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities or detachment from others.
Hyperarousal symptoms:
- Hypervigilance and an exaggerated startle response.
- Difficulty sleeping, irritability, or outbursts of anger.
- Problems with concentration or memory.
Diagnosis of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
Diagnosing PTSD involves a comprehensive assessment by a mental health professional. Key components of the diagnosis include:
- Meeting the diagnostic criteria outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5).
- Reporting symptoms that persist for more than one month and significantly impair daily functioning.
- Ruling out other potential causes for the symptoms.
Causes of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
PTSD can be caused by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. Several factors may contribute to the development of PTSD, including:
- Severity of the trauma: The more severe and prolonged the trauma, the higher the risk of developing PTSD.
- Personal factors: Individual characteristics, such as previous trauma, personal resilience, and coping mechanisms, can influence the development of PTSD.
- Brain and hormonal changes: Trauma can lead to alterations in brain structures and neurotransmitter levels, affecting the stress response.
Effects of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
PTSD can have significant effects on various aspects of an individual's life, including:
- Emotional impact: Feelings of fear, anxiety, depression, and emotional numbing.
- Relationship difficulties: Strained relationships, social withdrawal, and difficulty with intimacy.
- Occupational impairment: Difficulty concentrating, absenteeism, and decreased productivity.
- Physical health: Increased risk of health problems such as cardiovascular issues and chronic pain.
- Substance abuse: Some individuals with PTSD may turn to alcohol or drugs as a way to cope with symptoms.
Treatment of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
Effective treatments are available for PTSD and may involve a combination of approaches:
- Psychotherapy: Different types of therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR), can help individuals process and manage traumatic memories and symptoms.
- Medications: Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
- Supportive interventions: Support groups, peer support, and self-help strategies can provide additional support and coping mechanisms.
Prevention of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder:
While it may not always be possible to prevent PTSD, early intervention and support can be beneficial. Some preventive measures include:
- Accessing mental health support: Seeking professional help after a traumatic event can promote healthy coping and reduce the risk of developing PTSD.
- Building resilience: Engaging in stress reduction techniques, practicing self-care, and maintaining a supportive network can help build resilience in the face of adversity.
It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms of PTSD or seeking more information to consult mental health professionals for a comprehensive evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment.
References:
American Psychiatric Association. (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). American Psychiatric Publishing.
National Institute of Mental Health. (2021). Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. Retrieved from https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd/index.shtml
Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2019). Treatment of Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Retrieved from https://store.samhsa.gov/product/Treatment-of-Posttraumatic-Stress-Disorder-PTSD/SMA14-4884