4 Signs You May Have Sarcoma -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Sarcoma is a type of cancer that originates in the soft tissues or bones of the body. It can occur in various areas such as muscles, tendons, blood vessels, fat, and bones. Sarcomas are relatively rare but can be aggressive. Let's explore the symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention of sarcoma:
Symptoms of Sarcoma:
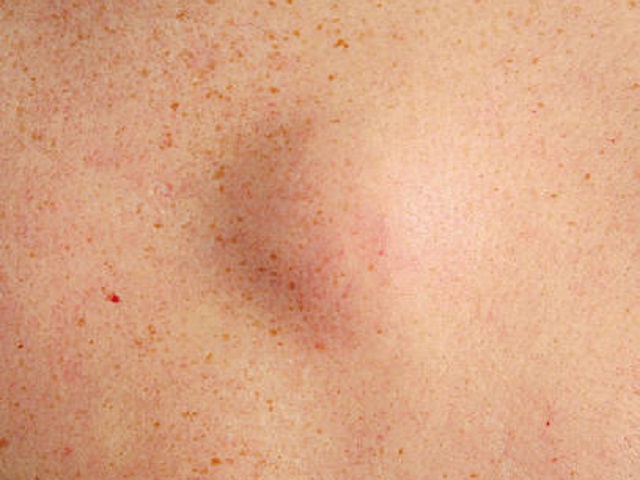
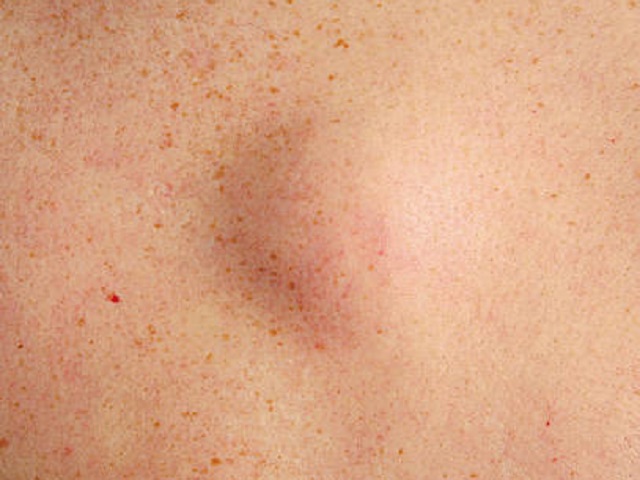
The symptoms of sarcoma may vary depending on the location and size of the tumor. Common signs and symptoms can include:
- A palpable lump or swelling in the affected area
- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Limited mobility or difficulty using the affected limb
- Fatigue and unexplained weight loss in advanced cases
Diagnosis of Sarcoma:
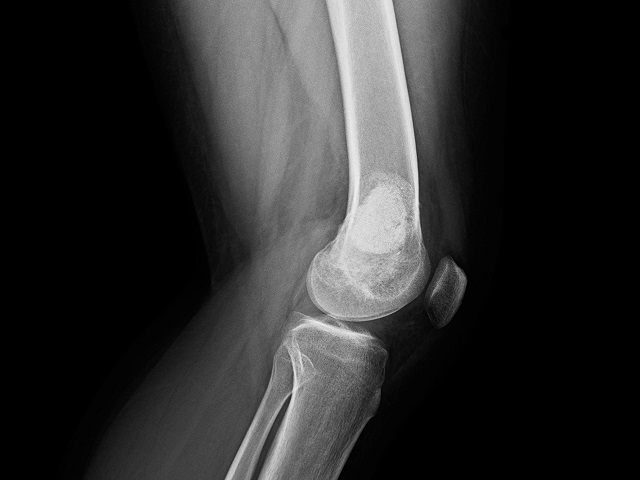
Diagnosing sarcoma involves several steps and tests. The following are commonly used diagnostic procedures:
- Medical history and physical examination: The doctor will review the patient's medical history, assess symptoms, and perform a physical examination.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI, or PET scans may be performed to visualize the tumor and determine its location, size, and extent.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is obtained from the tumor for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of sarcoma and determine its specific type.
- Pathology evaluation: A pathologist examines the biopsy sample under a microscope to determine the type, grade, and stage of the sarcoma.
Causes of Sarcoma:
The exact causes of sarcoma are often unknown, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing this type of cancer. These include:
- Genetic predisposition: Some individuals may inherit gene mutations that increase the risk of developing sarcoma.
- Radiation exposure: Previous radiation therapy for other cancers can slightly increase the risk of developing radiation-induced sarcoma.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain chemicals or toxins may contribute to the development of sarcoma, although specific links are not always clear.
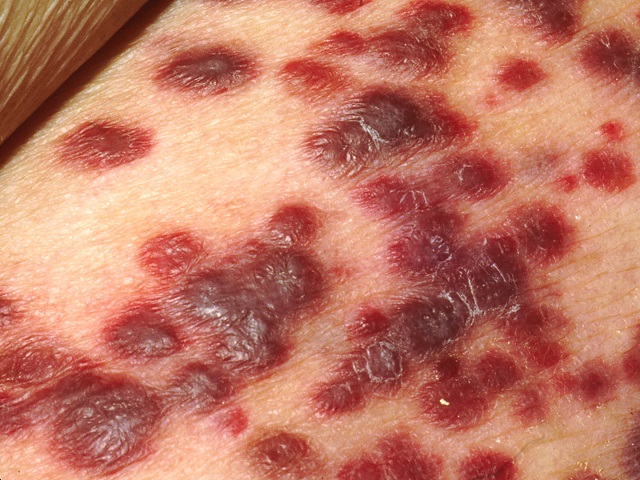
Effects of Sarcoma:
Sarcoma can have significant effects on the affected individual's health and quality of life. These may include:
- Localized symptoms such as pain, swelling, or functional impairment due to the tumor's presence and growth.
- Invasion and destruction of nearby tissues and structures, which can cause organ dysfunction or nerve compression.
- Potential spread (metastasis) to other parts of the body, leading to advanced disease and complications.
Treatment of Sarcoma:
The treatment of sarcoma depends on various factors, including the type, stage, and location of the tumor. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor is the primary treatment for sarcoma. In some cases, radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to improve outcomes.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy beams are used to target and kill cancer cells or shrink the tumor.
- Chemotherapy: Anti-cancer drugs may be used to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth, particularly for advanced or metastatic sarcoma.
- Targeted therapy: Some sarcomas may have specific genetic or molecular abnormalities that can be targeted with medications.
Prevention of Sarcoma:
Since the exact causes of sarcoma are often unknown, there are no specific prevention measures for the condition. However, general healthy lifestyle choices can potentially reduce the risk of developing any type of cancer. These include:
- Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
- Protecting oneself from harmful radiation sources.
- Being aware of any personal or family history of sarcoma or related conditions and discussing it with a healthcare professional.
References:
National Cancer Institute. (2021). Adult Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treatment (PDQ)�Patient Version. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/soft-tissue-sarcoma/patient/adult-soft-tissue-treatment-pdq