5 Signs You May Have Ewing's Sarcoma -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Ewing's sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects children and young adults. It is a malignant tumor that commonly arises in the bones but can also develop in soft tissues. It most commonly affects the long bones, such as the femur or tibia, but can also occur in the pelvis, ribs, and other locations. Here is an explanation of Ewing's sarcoma, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Ewing's Sarcoma:
The symptoms of Ewing's sarcoma can vary, but common signs and symptoms include:
- Bone pain: Persistent pain, swelling, or tenderness in the affected bone.
- Swelling or lump: A noticeable swelling or lump may develop over the affected area.
- Limited range of motion: Difficulty moving the affected limb or joint.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or weak.
- Fever: Low-grade fever may be present.
Diagnosis of Ewing's Sarcoma:
Diagnosing Ewing's sarcoma involves several methods to assess and confirm the presence of the tumor:
- Medical history and physical examination: A healthcare professional will inquire about symptoms, perform a physical examination, and evaluate the affected area for signs of a tumor.
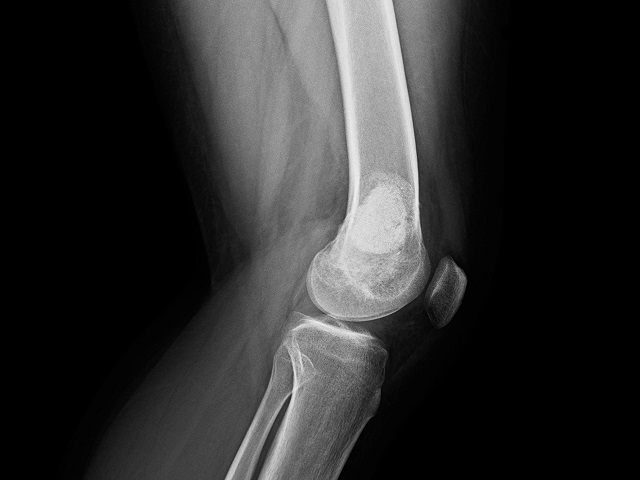
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as X-ray, MRI, CT scan, or bone scan may be used to visualize the tumor and assess its location and extent.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample from the tumor is collected for laboratory analysis to confirm the presence of Ewing's sarcoma cells.
Causes of Ewing's Sarcoma:
The exact cause of Ewing's sarcoma is unknown. However, researchers believe that genetic changes, specifically translocations involving chromosomes 11 and 22, play a role in the development of this cancer. Environmental factors and exposure to radiation may also contribute to the risk.
Effects of Ewing's Sarcoma:
If left untreated or undetected, Ewing's sarcoma can have severe effects on a person's health:
- Local spread: The tumor can invade surrounding tissues and nearby bones, causing destruction and affecting the function of affected organs or limbs.
- Metastasis: Ewing's sarcoma can spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, bones, or bone marrow, leading to more advanced stages of the disease and reduced survival rates.
Treatment of Ewing's Sarcoma:
The treatment of Ewing's sarcoma typically involves a multidisciplinary approach and may include:
- Chemotherapy: Powerful medications are administered to kill cancer cells and shrink the tumor before surgery or radiation therapy.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding affected tissues or bones is often performed, aiming for complete removal.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy X-rays or other radiation sources are used to kill cancer cells and reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Targeted therapy: Certain medications specifically designed to target genetic changes in Ewing's sarcoma cells may be used as part of the treatment plan.
Prevention of Ewing's Sarcoma:
As the causes of Ewing's sarcoma are not fully understood, there are no specific preventive measures. However, avoiding unnecessary exposure to radiation and adopting a healthy lifestyle may contribute to overall well-being.
It is important for individuals to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment, and prevention strategies related to Ewing's sarcoma.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2021). Ewing Tumors. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/ewing-tumor.html
National Cancer Institute. (2022). Ewing Sarcoma Treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/bone/hp/ewing-treatment-pdq
Orbach, D., Brennan, B., Bisogno, G., & van Noesel, M. M. (Eds.). (2019). Paediatric and Adolescent Osteosarcoma. Springer.
Image Attribution:
Featured image by Gianluca Cernicchiaro, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons