5 Signs You May Have Coronary Artery Disease -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. Here is an explanation of coronary artery disease, including its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention.
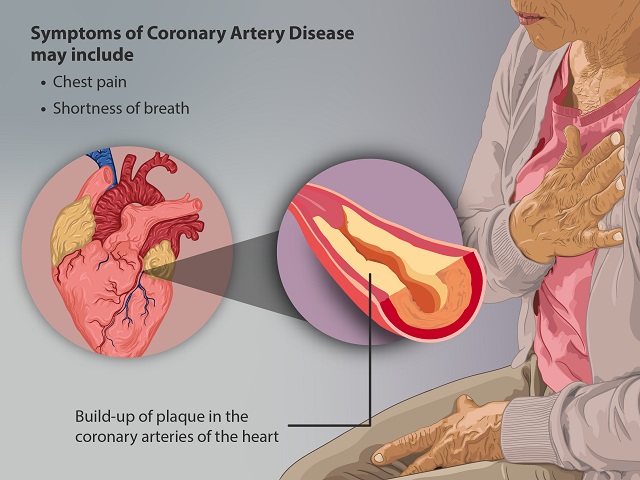
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease:
Coronary artery disease may not cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages, but as the condition progresses, individuals may experience the following:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Weakness or dizziness
Causes of Coronary Artery Disease:
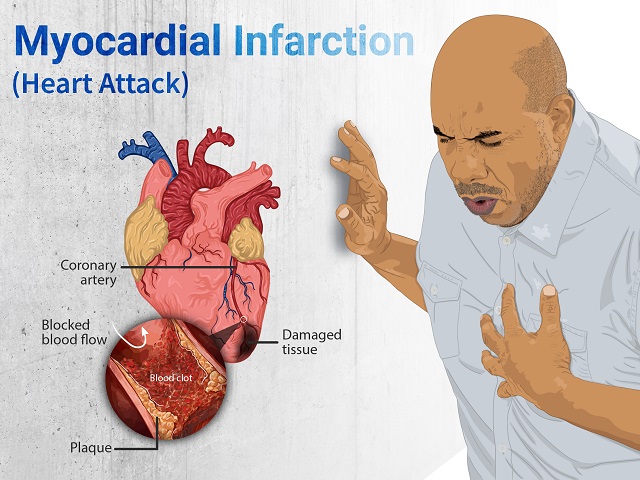
Coronary artery disease is primarily caused by the buildup of plaque within the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis. Several factors contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease, including:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Family history of heart disease
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Aging
Effects of Coronary Artery Disease:
Coronary artery disease can lead to various complications, including:
- Angina: Reduced blood flow to the heart can cause chest pain or discomfort during physical exertion or stress.
- Heart attack: A complete blockage of a coronary artery can result in a heart attack, leading to permanent heart muscle damage.
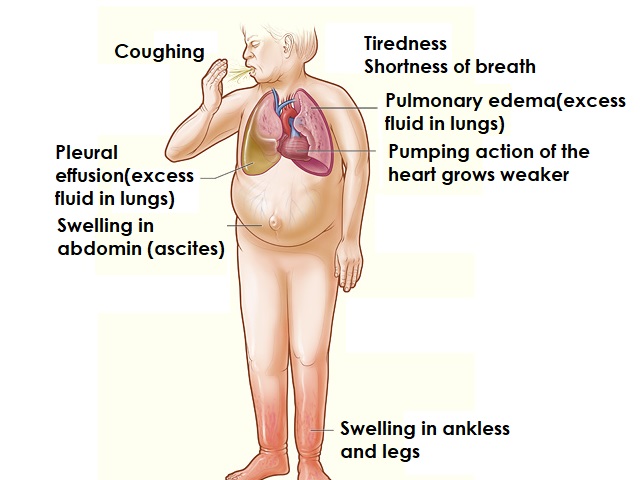
- Heart failure: The weakened heart muscle may not pump blood effectively, leading to heart failure.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms can occur due to the inadequate blood supply to the heart.
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease:
To diagnose coronary artery disease, healthcare professionals may perform the following:
- Physical examination and medical history
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Stress tests
- Coronary angiography
- Cardiac imaging tests (e.g., CT scan, MRI)
Treatment and Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease:
Treatment and prevention strategies for coronary artery disease focus on:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and weight management.
- Medications: Prescribed medications can help manage blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and prevent blood clots.
- Medical procedures: In some cases, medical procedures such as angioplasty, stent placement, or coronary artery bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and guidance on preventive measures.
References:
Mayo Clinic. (2020). Coronary Artery Disease. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/coronary-artery-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20350613
American Heart Association. (2021). Coronary Artery Disease. https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/consumer-healthcare/what-is-cardiovascular-disease/coronary-artery-disease
Image Attribution:
Featured image by https://www.myupchar.com/en, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons