7 Signs You May Have Heart Attack -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
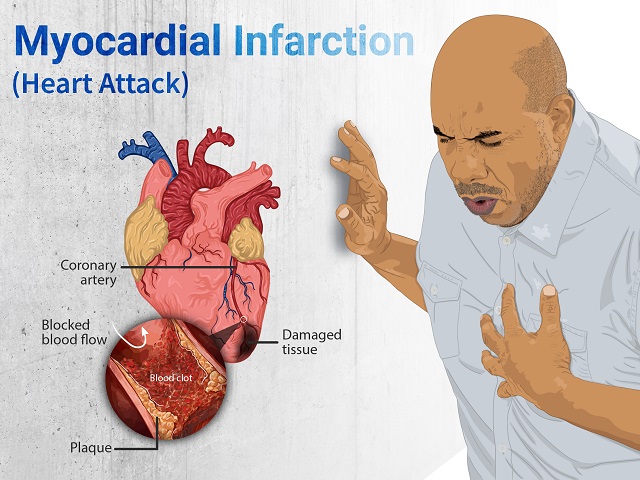
A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked, usually due to a blood clot. Here is an explanation of a heart attack, including its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention.
Symptoms of Heart Attack:
A heart attack may present with the following symptoms:
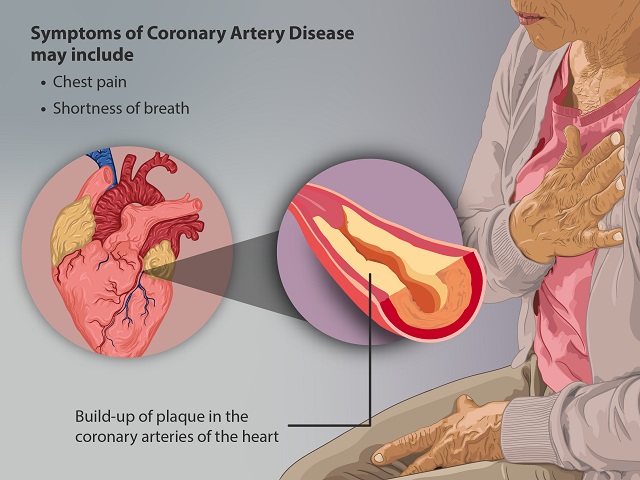
- Chest pain or discomfort, often described as a tightness, squeezing, or pressure
- Pain or discomfort radiating to the left arm, jaw, or back
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea, vomiting, or indigestion
- Cold sweat
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
Causes of Heart Attack:
The primary cause of a heart attack is the blockage of a coronary artery, usually by a blood clot. The underlying factors that contribute to the development of a heart attack include:
- Atherosclerosis: The buildup of fatty plaques in the coronary arteries, leading to narrowed or blocked arteries.
- Coronary artery spasm: Sudden contraction of the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow.
- Blood clot: Formation of a blood clot in a narrowed coronary artery, obstructing blood flow to the heart.
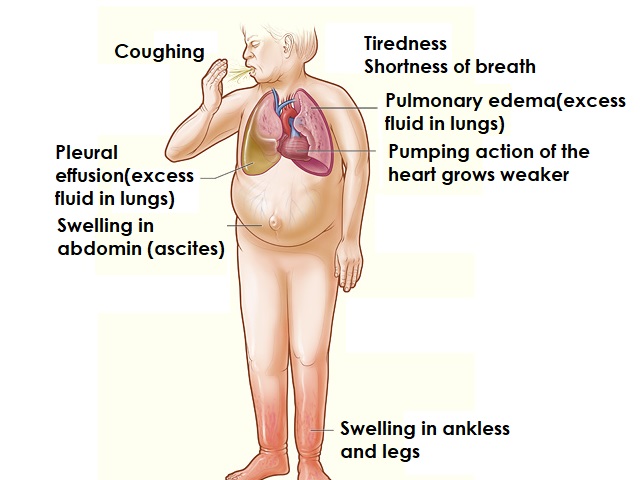
Effects of Heart Attack:
A heart attack can have severe consequences, including:
- Damage to the heart muscle: Lack of oxygen-rich blood can cause permanent damage to the heart muscle.
- Heart failure: Weakened heart muscle may result in the heart's inability to pump blood effectively.
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms may occur due to the disrupted electrical signaling in the heart.
Diagnosis of Heart Attack:
Healthcare professionals employ several methods to diagnose a heart attack, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Blood tests to measure cardiac enzymes and biomarkers
- Echocardiogram
- Cardiac catheterization
- Coronary angiography
Treatment and Prevention of Heart Attack:
Prompt medical intervention is crucial for the treatment of a heart attack. The following approaches are typically employed:
- Medications: Medications such as aspirin, clot-busting drugs, beta-blockers, and statins may be prescribed.
- Coronary angioplasty and stenting: A procedure to widen the blocked coronary artery and restore blood flow.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery: Surgical intervention to bypass blocked coronary arteries.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: A comprehensive program involving exercise, education, and counseling to aid recovery and prevent future heart problems.
- Preventive measures for heart attacks include lifestyle modifications and addressing risk factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, obesity, and diabetes.
References:
American Heart Association. (2021). Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction). https://www.heart.org/en/health-topics/heart-attack
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Heart Attack. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-attack/symptoms-causes/syc-20373106
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2021). Heart Attack. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/heart-attack
Image Attribution:
Featured image by https://www.myupchar.com/en, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons