7 Seven Signs You May Have HIV/AIDS -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a viral infection that attacks the immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), which are crucial for fighting off infections. Over time, HIV can weaken the immune system and progress to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), a more advanced stage of the infection.
Symptoms of HIV/AIDS:
The symptoms of HIV can vary from person to person and can resemble flu-like symptoms, including:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Sore throat
- Rash
- Headache
- Muscle and joint pain
As HIV progresses to AIDS, individuals may experience severe symptoms, such as persistent cough, rapid weight loss, recurring fever, night sweats, chronic diarrhea, and opportunistic infections.
Causes of HIV/AIDS:
HIV is primarily transmitted through:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse: Including vaginal, anal, or oral sex with an infected individual.
- Sharing needles: Sharing contaminated needles or syringes during drug use.
- From mother to child: HIV can be transmitted during pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
Effects of HIV/AIDS:
Without proper treatment, HIV can lead to severe complications and opportunistic infections due to a weakened immune system. These can include:
- Opportunistic infections: Infections that take advantage of a weakened immune system, such as tuberculosis, pneumonia, and certain types of cancers.
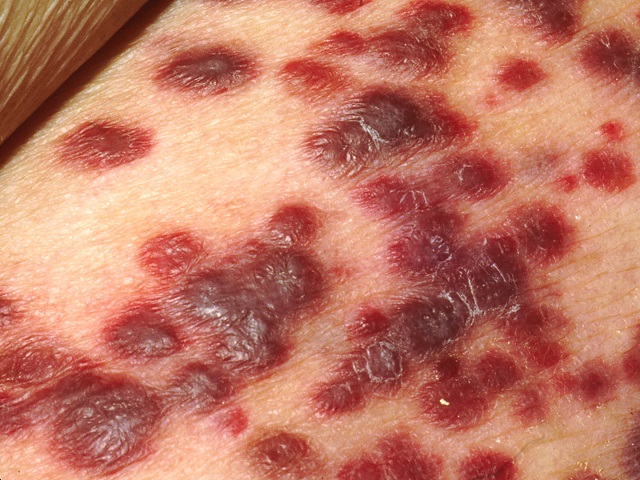
- AIDS-defining illnesses: These are specific infections or conditions that indicate advanced HIV infection, such as Kaposi's sarcoma, lymphoma, and severe recurrent pneumonia.
Treatment and Prevention of HIV/AIDS:
There is currently no cure for HIV/AIDS, but with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, people living with HIV can manage the infection and lead long, healthy lives. The treatment of HIV/AIDS typically involves antiretroviral therapy (ART), which helps suppress the virus, slow down the progression of the disease, and prevent transmission.
Prevention strategies for HIV/AIDS include:
- Safe sex practices: Using condoms consistently and correctly during sexual intercourse can reduce the risk of HIV transmission.
- Needle exchange programs: Avoid sharing needles or syringes and use clean equipment for drug use.
- HIV testing and counseling: Regular HIV testing, particularly for individuals at high risk, can help detect the infection early and facilitate timely treatment.
- It is important to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and prevention strategies for HIV/AIDS.
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021a). HIV basics. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/basics/index.html
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021b). HIV/AIDS. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/hiv/default.html