5 Signs You May Have Anal Cancer -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
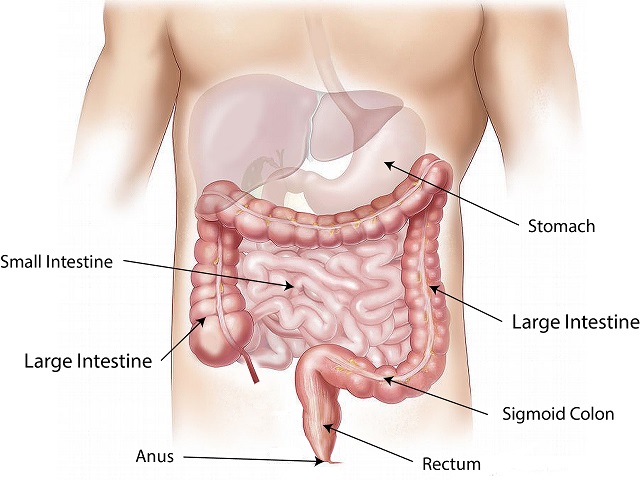
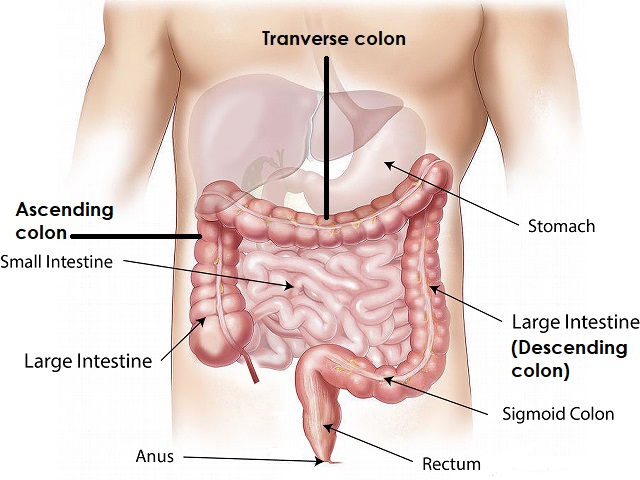
Anal cancer is a rare form of cancer that develops in the tissues of the anus. It usually begins in the cells lining the anal canal and can potentially spread to nearby lymph nodes and other parts of the body. Here is a brief explanation of anal cancer, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Anal Cancer:
The symptoms of anal cancer can include:
- Anal bleeding or discharge: Persistent bleeding from the anus or the presence of unusual discharge.
- Anal pain or discomfort: Persistent pain or discomfort in the anal area.
- Itching or irritation: Persistent itching or irritation in the anal region.
- Changes in bowel movements: Changes in bowel habits, including diarrhea or constipation.
- Lumps or masses: The presence of a lump or mass near the anus or in the anal canal.
Diagnosis of Anal Cancer:
Diagnosing anal cancer involves several methods to evaluate the presence and extent of the disease:
- Physical examination: A healthcare professional may perform a physical examination of the anus and rectum to check for any abnormalities or lumps.
- Anal Pap test: Similar to a Pap test for cervical cancer, an anal Pap test involves collecting cells from the anus to check for abnormal changes.
- Biopsy: If abnormal cells or masses are found, a biopsy may be performed to obtain tissue samples for further examination and confirmation of cancerous cells.
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as MRI, CT scan, or PET scan may be used to determine the extent of cancer and identify if it has spread to other parts of the body.
Causes of Anal Cancer:
Several factors may contribute to the development of anal cancer:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Infection with certain types of HPV, especially HPV-16 and HPV-18, is a significant risk factor for anal cancer.
- Weakened immune system: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or who have undergone organ transplantation, are at higher risk.
- Anal intercourse: Engaging in receptive anal intercourse can increase the risk of anal cancer, especially in individuals with HPV infection.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoking has been associated with an increased risk of anal cancer.
Effects of Anal Cancer:
If left untreated or undetected, anal cancer can have serious effects on an individual's health:
- Metastasis: Anal cancer can spread to nearby lymph nodes and other organs, leading to more advanced stages of the disease and reduced survival rates.
- Impact on quality of life: Anal cancer and its treatments can cause physical discomfort, pain, changes in bowel function, and emotional distress, affecting the overall quality of life.
Treatment of Anal Cancer:
The treatment of anal cancer depends on the stage and extent of the disease and may involve a combination of approaches:
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy is the primary treatment for anal cancer and involves using high-energy X-rays or other radiation sources to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used in combination with radiation therapy (chemoradiotherapy) or as the primary treatment for more advanced cases of anal cancer.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be performed to remove the cancerous tissue, nearby lymph nodes, or to create a colostomy or ileostomy, depending on the location and extent of the cancer.
Prevention of Anal Cancer:
While it may not be possible to prevent anal cancer entirely, certain measures may help reduce the risk:
- HPV vaccination: The HPV vaccine can protect against the types of HPV that are associated with anal cancer.
- Safe sexual practices: Practicing safe sex, including using condoms and reducing the number of sexual partners, may reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking can reduce the risk of developing anal cancer.
If you experience any symptoms or have concerns, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2021). Anal Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/anal-cancer.html
National Cancer Institute. (2022). Anal Cancer Treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/anal/hp/anal-treatment-pdq
American Society of Clinical Oncology. (2022). Anal Cancer: Risk Factors and Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/anal-cancer/risk-factors-and-prevention