5 Signs You May Have Colon Cancer -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
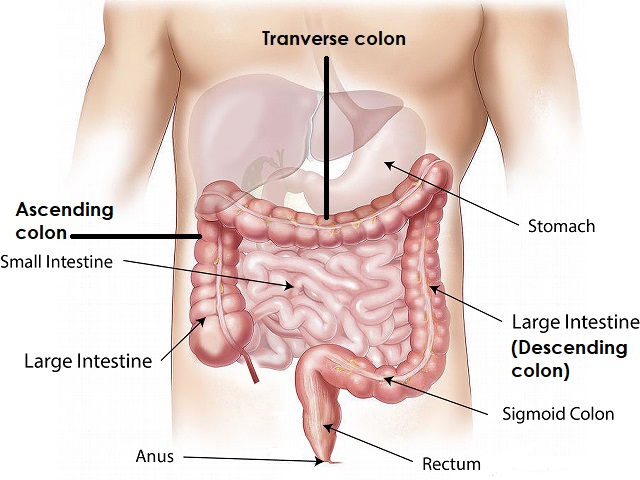
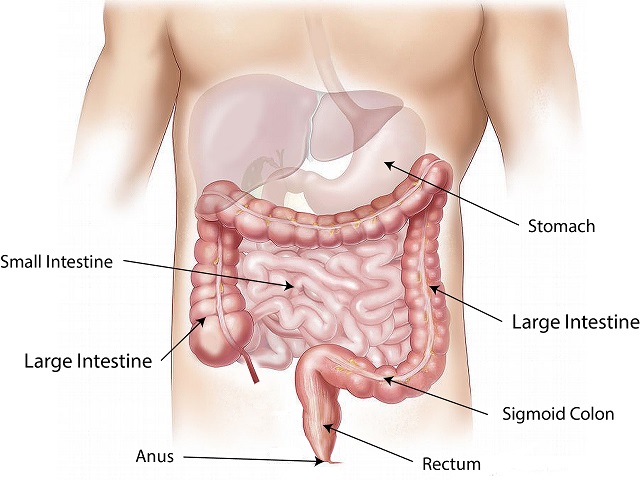
Colon cancer, also known as colorectal cancer, is a type of cancer that affects the colon or rectum. It is a malignant tumor that develops in the colon or rectum It typically originates from abnormal growths called polyps in the lining of the colon or rectum. Over time, these polyps can become cancerous and potentially spread to other parts of the body. Here is an explanation of colon cancer, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Colon Cancer:
The symptoms of colon cancer can vary, but common signs and symptoms include:
- Changes in bowel habits: Persistent changes in bowel movements, such as diarrhea, constipation, or a change in stool consistency.
- Rectal bleeding: Blood in the stool or bleeding from the rectum.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort: Cramping, pain, or bloating in the abdomen.
- Weakness or fatigue: Unexplained weakness or fatigue.
- Unintentional weight loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss.
Diagnosis of Colon Cancer:
The diagnosis of colon cancer involves several methods to assess and confirm the presence of cancer:
- Screening tests: Common screening tests for colon cancer include colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and fecal occult blood tests, which can detect polyps or abnormal cells in the colon or rectum.
- Biopsy: If suspicious growths or abnormalities are detected during screening, a biopsy may be performed to obtain tissue samples for further analysis and confirmation of cancerous cells.
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques such as CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans may be used to determine the extent of cancer and identify if it has spread to other parts of the body.
Causes of Colon Cancer:
The exact causes of colon cancer are not fully understood, but certain factors may increase the risk:
- Age: The risk of colon cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in individuals over 50.
- Family history: Having a family history of colon cancer or certain genetic syndromes can increase the risk.
- Personal history of polyps or inflammatory bowel disease: Individuals with a history of polyps or inflammatory bowel disease are at higher risk.
- Lifestyle factors: Unhealthy lifestyle habits, such as a diet high in red and processed meats, low fiber intake, sedentary lifestyle, obesity, and smoking, may increase the risk.
Effects of Colon Cancer:
Colon cancer can have significant effects on an individual's health and well-being:
- Metastasis: If left untreated or undetected, colon cancer can spread to other organs and tissues, leading to more severe complications and reduced survival rates.
- Impact on quality of life: Colon cancer and its treatments can cause physical discomfort, pain, fatigue, and emotional distress, affecting the overall quality of life.
Treatment of Colon Cancer:
The treatment of colon cancer depends on the stage and extent of the disease but often involves a combination of approaches:
- Surgery: The primary treatment for colon cancer involves surgical removal of the tumor and nearby affected tissue, along with nearby lymph nodes.
- Chemotherapy: In cases where cancer has spread or is at high risk of recurrence, chemotherapy may be recommended to kill cancer cells or reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used in specific cases to target and destroy cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy: These newer treatment approaches may be used in advanced cases to target specific molecular abnormalities or boost the body's immune system against cancer cells.
Prevention of Colon Cancer:
Several measures can help reduce the risk of colon cancer or detect it at an early stage:
- Screening: Regular screening for colon cancer, especially for individuals aged 50 and above or those at higher risk, can help detect and remove polyps before they become cancerous.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can reduce the risk.
- Genetic counseling: Individuals with a family history of colon cancer or certain genetic syndromes may benefit from genetic counseling and testing to understand their risk and take appropriate preventive measures.
It is important for individuals to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment, and prevention strategies for colon cancer.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2021). Colorectal Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/colon-rectal-cancer.html
National Cancer Institute. (2022). Colon Cancer Treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/hp/colon-treatment-pdq
American Society of Clinical Oncology. (2022). Colon Cancer: Risk Factors and Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/colorectal-cancer/risk-factors-and-prevention