10 Signs You May Have Liver Cancer -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is a type of cancer that originates in the liver. It is a serious condition that can have significant health consequences. Here is an explanation of liver cancer, including its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer:
The symptoms of liver cancer may include:
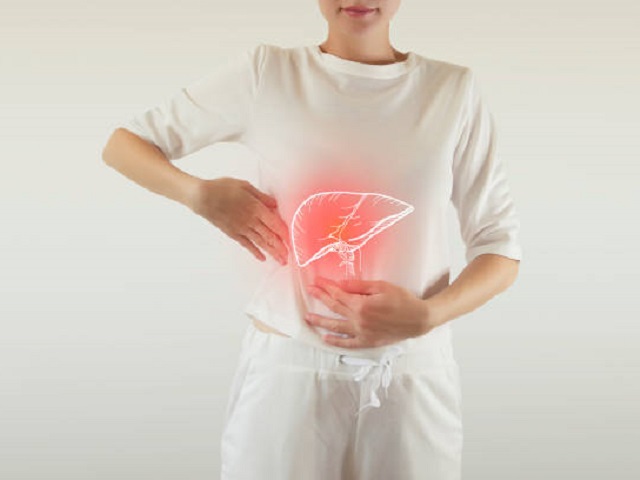
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Unintentional weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
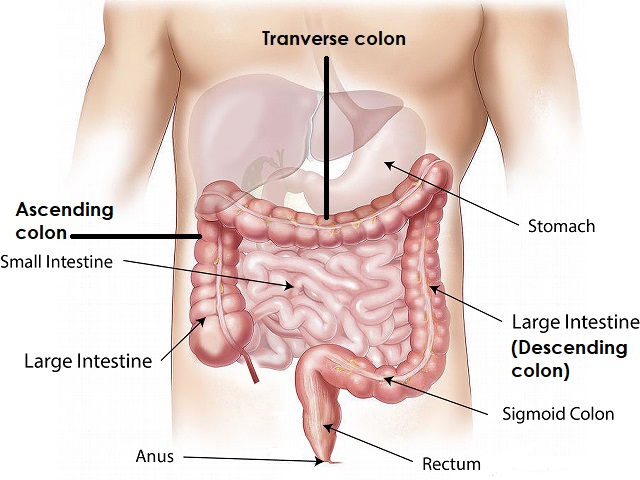
- Abdominal swelling or fluid buildup
- Nausea and vomiting
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Enlarged liver
- Changes in the color of urine or stool
Diagnosis of Liver Cancer:
The diagnosis of liver cancer involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. The following assessments and tests are commonly used:
- Blood tests: To measure liver function and identify tumor markers.
- Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, to visualize the liver and detect any abnormalities or tumors.
- Biopsy: A small sample of liver tissue is obtained for analysis to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Angiography: A procedure that uses contrast dye to create detailed images of blood vessels in the liver.
Causes of Liver Cancer:
Liver cancer can have multiple causes, including:
- Chronic viral hepatitis: Infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) significantly increases the risk of developing liver cancer.
- Cirrhosis: Long-term liver damage and scarring, often caused by alcohol abuse, chronic viral hepatitis, or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), can lead to the development of liver cancer.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Accumulation of fat in the liver, usually associated with obesity, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, can progress to liver cancer in some cases.
- Genetic factors: Certain inherited liver conditions, such as hemochromatosis and Wilson disease, can increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to certain toxins and chemicals, such as aflatoxins, vinyl chloride, and arsenic, can contribute to the development of liver cancer.
Effects of Liver Cancer:
Liver cancer can have profound effects on overall health, including:
- Impaired liver function: The presence of cancerous tumors can interfere with the liver's ability to perform essential functions, such as detoxification, metabolism, and protein synthesis.
- Complications: Liver cancer can lead to complications such as liver failure, bleeding, fluid buildup in the abdomen (ascites), and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Spread to other organs: Advanced liver cancer can metastasize, spreading to other organs such as the lungs, bones, or lymph nodes.
Treatment of Liver Cancer:
The treatment of liver cancer depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, overall health, and individual circumstances. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor or liver transplantation may be considered for early-stage liver cancer.
- Ablation therapy: Techniques such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), or cryoablation can be used to destroy the cancerous tissue.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy beams are targeted at the tumor to kill cancer cells or slow down their growth.
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE): Chemotherapy drugs are injected directly into the blood vessels that supply the tumor, followed by embolization to cut off its blood supply.
- Targeted therapy: Medications that specifically target cancer cells or the molecular changes associated with liver cancer may be prescribed.
- Immunotherapy: Treatment that helps the body's immune system recognize and attack cancer cells.
- Palliative care: Supportive care to manage symptoms and improve quality of life, often provided in advanced stages of liver cancer.
Prevention of Liver Cancer:
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of liver cancer, certain measures can reduce the risk:
- Hepatitis vaccination: Vaccination against hepatitis B virus (HBV) can significantly lower the risk of liver cancer.
- Safe sex practices: Practicing safe sex and avoiding multiple sexual partners can help reduce the risk of hepatitis B and C infection.
- Prevention of hepatitis transmission: Taking precautions to prevent the transmission of hepatitis B and C, such as avoiding sharing needles and practicing safe hygiene, can reduce the risk.
- Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is a known risk factor for liver cancer. Limiting alcohol intake can help lower the risk.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help prevent obesity and reduce the risk of liver cancer.
- Avoid exposure to toxins: Minimize exposure to environmental toxins, such as aflatoxins, vinyl chloride, and arsenic, which can increase the risk of liver cancer.
Please it is important to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment plans, and up-to-date information.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2021). Liver Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/liver-cancer.html
Llovet, J. M., et al. (2018). Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature Reviews Disease Primers, 4(1), 18035. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2018.35
Singal, A. G., et al. (2019). Diagnosis and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology, 68(2), 723�750. DOI: 10.1002/hep.29913