7 Signs You May Have Arthritis -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
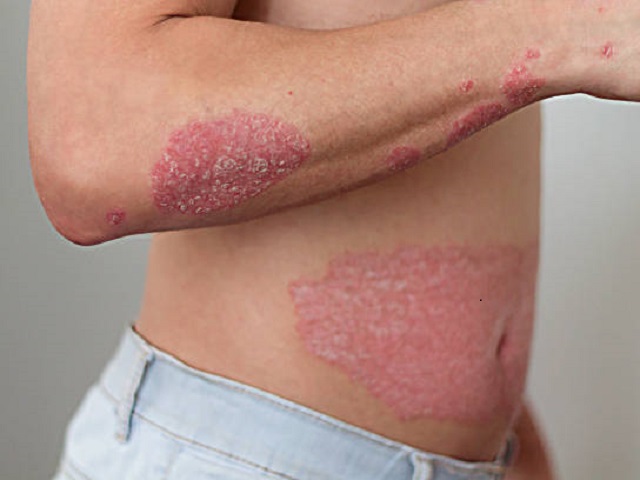
Arthritis refers to a group of conditions characterized by inflammation and stiffness in the joints, leading to pain, swelling, and limited mobility. It is a common chronic condition that can affect people of all ages, with different types of arthritis having varying causes and manifestations.
Symptoms of Arthritis
The symptoms of arthritis can vary depending on the type and severity of the condition, but they generally include:
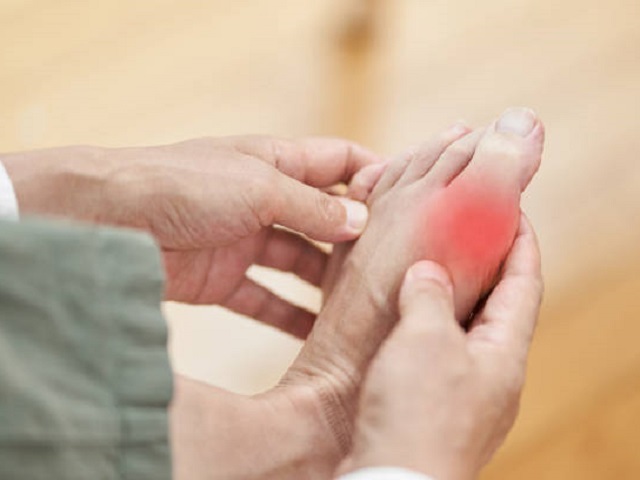
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Swelling and redness around the joints
- Stiffness and decreased range of motion
- Joint warmth
- Fatigue and general malaise
- Morning stiffness that lasts for more than an hour
- Weakness and muscle wasting in advanced cases
Causes of Arthritis
Arthritis can have multiple causes, including:
- Age-related wear and tear on the joints (osteoarthritis)
- Autoimmune disorders that cause the immune system to attack the joints (rheumatoid arthritis)
- Inflammatory response to infections (infectious arthritis)
- Uric acid crystal accumulation in the joints (gout)
- Injury or trauma to the joints
- Genetic predisposition to certain types of arthritis
- Abnormal metabolism leading to joint damage (e.g., in psoriatic arthritis)
Effects of Arthritis
Arthritis can have significant effects on an individual's daily life and overall well-being, including:
- Chronic pain and discomfort
- Reduced mobility and difficulty performing daily activities
- Joint deformities and functional limitations
- Decreased quality of life and overall physical and mental health
- Increased risk of falls and fractures
- Emotional distress, such as anxiety and depression
Treatment of Arthritis
The treatment of arthritis aims to manage symptoms, improve joint function, and slow disease progression. Treatment options may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and biologic agents.
- Physical therapy: Exercises, stretches, and techniques to improve joint flexibility, strengthen muscles, and reduce pain.
- Assistive devices: Braces, splints, canes, or orthotics to support joint function and relieve pressure.
- Lifestyle modifications: Weight management, regular exercise, and joint protection techniques.
- Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements may provide some relief, but their effectiveness varies.
- Surgery: In severe cases, joint replacement surgery or joint fusion may be considered.
Prevention of Arthritis
While certain types of arthritis cannot be prevented, some measures can help reduce the risk or delay the onset of arthritis:
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen muscles and support joint health.
- Protect joints from injury by using proper techniques during physical activities.
- Practice good posture and ergonomics to minimize strain on joints.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids to support joint health.
- Quit smoking, as it increases the risk and severity of certain types of arthritis.
- It's important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plan, and guidance on managing arthritis.
References:
Arthritis. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/arthritis/symptoms-causes/syc-20350772
Arthritis. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/index.htm