7 Signs You May Have Cystic fibrosis -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
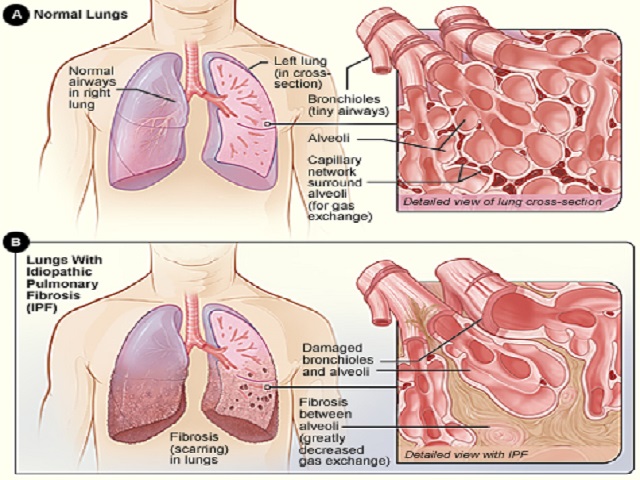
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the lungs and digestive system. It is characterized by the production of thick, sticky mucus that can obstruct the airways, impair lung function, and lead to various complications.
Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
The symptoms of cystic fibrosis can vary, but some common signs include:
- Persistent cough with thick mucus
- Frequent respiratory infections, such as pneumonia and bronchitis
- Wheezing or shortness of breath
- Poor weight gain and growth despite a good appetite
- Greasy, bulky stools and difficulty absorbing nutrients
- Nasal congestion or sinusitis
- Clubbing of fingers and toes (enlargement and rounding of the fingertips)
Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is typically diagnosed through a combination of tests, including:
- Newborn screening: A blood test performed shortly after birth to detect elevated levels of a protein called immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT), which may indicate cystic fibrosis.
- Sweat test: This measures the amount of salt in sweat, as people with CF tend to have higher salt levels. It is considered the gold standard diagnostic test.
- Genetic testing: Analyzing DNA samples to identify mutations in the CFTR gene responsible for cystic fibrosis.
Causes of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene. These mutations affect the production and function of the CFTR protein, which is responsible for regulating the movement of salt and fluids in and out of cells. The faulty CFTR protein leads to the buildup of thick, sticky mucus in various organs.
Effects of Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis can have profound effects on multiple body systems, including:
- Respiratory system: The thick mucus obstructs the airways, leading to chronic lung infections, inflammation, and progressive lung damage.
- Digestive system: The mucus can block the pancreatic ducts, impairing the release of digestive enzymes and causing malabsorption of nutrients.
- Liver: Some individuals with cystic fibrosis may develop liver disease, including hepatobiliary disorders and cirrhosis.
- Reproductive system: Men with CF may have a congenital absence of the vas deferens (the tubes that carry sperm), leading to infertility. Women may experience reduced fertility due to thick cervical mucus.
Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
Although there is no cure for cystic fibrosis, treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
- Airway clearance techniques: Techniques such as chest physiotherapy, positive expiratory pressure devices, and oscillatory devices help loosen and clear mucus from the airways.
- Medications: Inhalers, antibiotics, pancreatic enzymes, and other medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms, prevent infections, and improve digestion.
- Nutritional support: A high-calorie, well-balanced diet and nutritional supplements may be recommended to meet the body's nutritional needs.
- Lung transplant: In severe cases, a lung transplant may be considered for individuals with advanced lung disease.
- Gene therapies: Experimental therapies aimed at correcting the underlying genetic mutations are being researched.
Prevention of Cystic Fibrosis
Since cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder, it cannot be prevented. However, carrier screening and genetic counseling are available to individuals with a family history of cystic fibrosis or those planning to have children to understand the risk of passing the condition to their offspring.
Note: The information provided is a brief overview of cystic fibrosis. For detailed and personalized information, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional.
References:
Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. (n.d.). About Cystic Fibrosis. Retrieved from https://www.cff.org/What-is-CF/About-Cystic-Fibrosis/
Mayo Clinic. (2022). Cystic Fibrosis. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cystic-fibrosis/symptoms-causes/syc-20353700
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2021). What Is Cystic Fibrosis? Retrieved from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/cystic-fibrosis