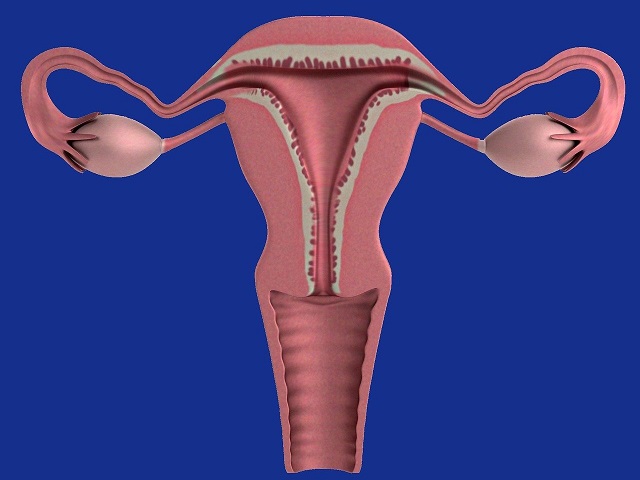
7 Signs You May Have Ovarian cysts -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or within the ovaries, which are part of the female reproductive system. Most ovarian cysts are benign and do not cause symptoms, but in some cases, they can lead to discomfort and complications.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cysts
While many ovarian cysts do not cause symptoms, some women may experience the following signs and symptoms:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Bloating or pressure in the abdomen
- Changes in menstrual patterns
- Pain during intercourse
- Frequent urination
- Difficulty emptying the bladder completely
- Nausea or vomiting
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be associated with other gynecological conditions, so a proper medical evaluation is necessary to diagnose ovarian cysts.
Causes of Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts can develop for various reasons, including:
- Follicle cysts: The most common type of ovarian cysts form when the follicle, which normally releases an egg during ovulation, does not rupture and continues to grow.
- Corpus luteum cysts: These cysts occur when the follicle releases an egg but the sac does not dissolve as it should, leading to fluid accumulation.
- Endometriomas: In some cases, tissue similar to the lining of the uterus can develop on the ovaries, forming cysts known as endometriomas.
- Cystadenomas: These cysts develop from the surface of the ovary and can be filled with fluid or mucus.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): PCOS is a hormonal disorder that can cause the ovaries to develop numerous small cysts.
Effects of Ovarian Cysts
Most ovarian cysts are harmless and resolve on their own without causing significant complications. However, in certain situations, ovarian cysts can lead to:
- Ovarian torsion: Large cysts or those that cause the ovary to twist can result in severe abdominal pain and may require immediate medical attention.
- Rupture: If a cyst ruptures, it can cause sudden and sharp pain, potentially leading to internal bleeding or infection.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
Treatment for ovarian cysts depends on factors such as the size, type, and symptoms experienced. Options may include:
- Watchful waiting: In cases where the cyst is small, fluid-filled, and causing no symptoms, a "wait and see" approach may be recommended.
- Medications: Hormonal contraceptives or other medications can help regulate the menstrual cycle, prevent the formation of new cysts, or shrink existing ones.
- Surgery: If a cyst is large, causing symptoms, or suspected to be cancerous, surgical intervention may be necessary. The cyst can be removed (cystectomy) or, in some cases, the entire ovary may need to be removed (oophorectomy).
Prevention of Ovarian Cysts
It's not always possible to prevent ovarian cysts, but the following measures may help reduce the risk or manage existing cysts:
- Regular gynecological exams: Routine check-ups allow for the early detection and monitoring of any ovarian cysts.
- Hormonal contraceptives: Certain birth control methods, such as combined oral contraceptives, can help regulate hormone levels and prevent the formation of some types of ovarian cysts.
- Prompt medical evaluation: Seek medical attention if you experience persistent pelvic pain or any unusual symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications.
Note: The information provided is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis, evaluation, and personalized treatment.
References:
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Ovarian cysts. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ovarian-cysts/symptoms-causes/syc-20353405
Office on Women's Health. (2019). Ovarian Cysts Fact Sheet. Retrieved from https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/ovarian-cysts
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2019). FAQ074: Ovarian Cysts. Retrieved from https://www.acog.org/womens-health/faqs/ovarian-cysts