6 Signs You May Have Ovarian Cancer --Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
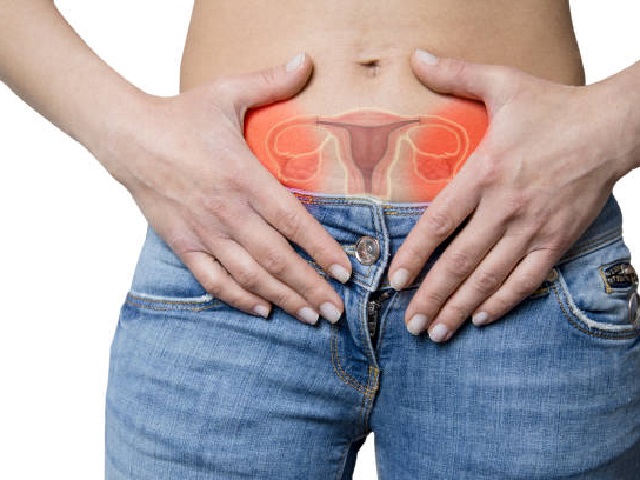
Ovarian cancer refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the ovaries, which are the female reproductive organs responsible for producing eggs. It is the fifth most common cancer among women and is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when it has spread beyond the ovaries.
Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
The symptoms of ovarian cancer can be vague and non-specific, making it challenging to diagnose in its early stages. Common symptoms may include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Pelvic discomfort or pain
- Feeling full quickly when eating
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or frequent urination
- Loss of appetite or unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue and low energy
It's important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions. If these symptoms persist for an extended period or worsen, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The exact causes of ovarian cancer are unknown, but certain factors may increase the risk of developing the disease:
- Age: The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age, with most cases occurring in women over 50.
- Family history: Women with close relatives (such as a mother, sister, or daughter) who have had ovarian cancer or breast cancer may have an increased risk.
- Inherited gene mutations: Inherited gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, are associated with a higher risk of developing ovarian cancer.
- Hormonal factors: Factors that increase the number of times a woman ovulates, such as starting menstruation at an early age or late menopause, may increase the risk.
- Reproductive history: Women who have never been pregnant or have had difficulty conceiving may have a slightly higher risk.
Effects of Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer can have various effects on a woman's health and well-being:
- Physical impact: The disease and its treatments can cause physical symptoms, such as abdominal pain, bloating, and weight loss. Advanced-stage ovarian cancer can spread to other organs, leading to further complications.
- Emotional and psychological impact: Coping with a cancer diagnosis and undergoing treatment can be emotionally challenging. Feelings of fear, anxiety, and depression are common.
- Fertility concerns: Ovarian cancer and its treatment may affect fertility. Discussing fertility preservation options with a healthcare provider before treatment is important for those desiring future pregnancies.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
The treatment of ovarian cancer depends on the stage and extent of the disease. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: The primary treatment involves the removal of the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and surrounding lymph nodes (debulking surgery). In some cases, additional surgery may be performed after chemotherapy to remove any remaining cancerous tissue.
- Chemotherapy: The use of anticancer drugs to destroy cancer cells. Chemotherapy can be administered before or after surgery and may involve a combination of different drugs.
- Targeted therapy: Certain medications that specifically target cancer cells' unique characteristics may be used in advanced cases.
- Radiation therapy: It is rarely used in ovarian cancer but may be employed in specific situations, such as palliative care to relieve symptoms.
Prevention of Ovarian Cancer
While it is not possible to prevent ovarian cancer entirely, there are measures that may help reduce the risk:
- Oral contraceptives: Long-term use of birth control pills has been associated with a reduced risk of ovarian cancer.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Women who have had full-term pregnancies and breastfed may have a lower risk.
- Genetic counseling and testing: Women with a family history of ovarian or breast cancer may consider genetic counseling and testing to assess their risk and take appropriate preventive measures.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on risk assessment, screening, and preventive strategies.
Note: The information provided is for educational purposes and should not replace professional medical advice. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalized guidance.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2021). Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/ovarian-cancer.html
Mayo Clinic. (2021). Ovarian Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ovarian-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20375941