8 Signs You May Have Acute Kidney Injury -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Image by CDC, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
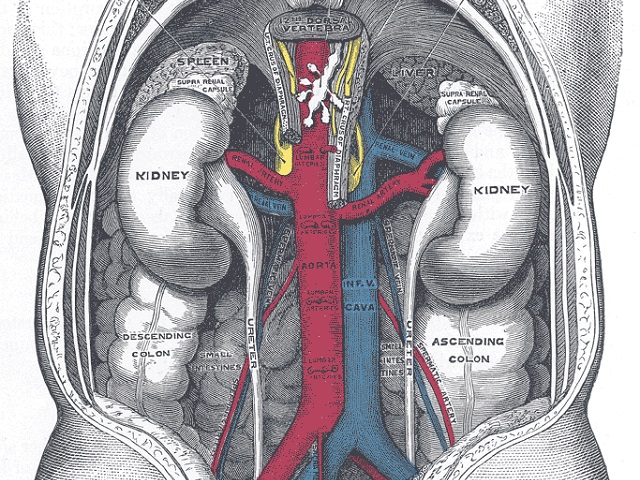
Acute kidney injury (AKI), also known as acute renal failure, refers to a sudden and rapid decline in kidney function. It is characterized by the inability of the kidneys to effectively filter waste products and excess fluid from the blood. AKI can be caused by various factors and can have serious implications on overall health.
Symptoms of Acute Kidney Injury:
The symptoms of acute kidney injury may include:
- Decreased urine output or no urine production
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet
- Fatigue or weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea or vomiting
- Confusion or disorientation
- Chest pain or pressure
- Seizures or coma (in severe cases)
Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury:
Diagnosing acute kidney injury involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and laboratory tests. The following assessments and tests are typically performed:
- Blood tests: Measuring levels of creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) to assess kidney function.
- Urine tests: Analyzing urine samples for abnormalities in protein levels, red and white blood cells, and electrolytes.
- Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound or CT scans, to evaluate the structure and size of the kidneys.
- Kidney biopsy: In some cases, a small tissue sample may be taken for further analysis.
Causes of Acute Kidney Injury:
Acute kidney injury can be caused by various factors, including:
- Decreased blood flow to the kidneys due to low blood pressure, dehydration, heart failure, or severe infections.
- Kidney damage from medications, toxins, or contrast dyes used in medical imaging procedures.
- Urinary tract obstruction, such as kidney stones or an enlarged prostate.
- Autoimmune disorders, such as vasculitis or glomerulonephritis.
- Severe infections, particularly those affecting the kidneys.
- Direct injury to the kidneys, such as trauma or surgery.
Effects of Acute Kidney Injury:
Acute kidney injury can have significant effects on the body, including:
- Fluid and electrolyte imbalances
- Accumulation of waste products and toxins in the body
- Acid-base imbalances
- Impaired regulation of blood pressure
- Metabolic disturbances
- Increased risk of complications and organ dysfunction
- Long-term kidney damage or chronic kidney disease (in some cases)
Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury:
The treatment of acute kidney injury focuses on addressing the underlying cause, supporting kidney function, and preventing complications. Treatment options may include:
- Fluid resuscitation to restore adequate blood flow and hydration.
- Medications to manage blood pressure, control infections, or address specific underlying conditions.
- Dialysis or kidney replacement therapy in severe cases to help remove waste products and excess fluid from the body.
- Nutritional support and electrolyte management.
- Management of complications and associated conditions.
- Close monitoring of kidney function and overall health.
Prevention of Acute Kidney Injury:
Preventing acute kidney injury involves:
- Maintaining proper hydration and fluid balance.
- Using medications responsibly and under medical supervision.
- Avoiding exposure to toxins and harmful substances.
- Managing underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure.
- Promptly treating infections and other conditions that may affect kidney function.
It is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and management of acute kidney injury.
References:
KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney International Supplements, 2(1), 1-138. DOI: 10.1038/kisup.2011.1
Kellum, J. A., et al. (2012). Diagnosis, evaluation, and management of acute kidney injury: A KDIGO summary (Part 1). Critical Care, 17(1), 204. DOI: 10.1186/cc11454
Mehta, R. L., et al. (2015). Acute kidney injury network: Report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Critical Care, 11(2), R31. DOI: 10.1186/cc5713