8 Signs You May Have Kidney Failure -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure, refers to a condition in which the kidneys are unable to perform their essential functions adequately. This leads to the accumulation of waste products and fluid imbalances in the body. Kidney failure can be acute or chronic.
Symptoms of Kidney Failure:
The symptoms of kidney failure may vary depending on the stage and underlying cause. Common symptoms include:
- Decreased urine output or changes in urine color and consistency.
- Fatigue and weakness.
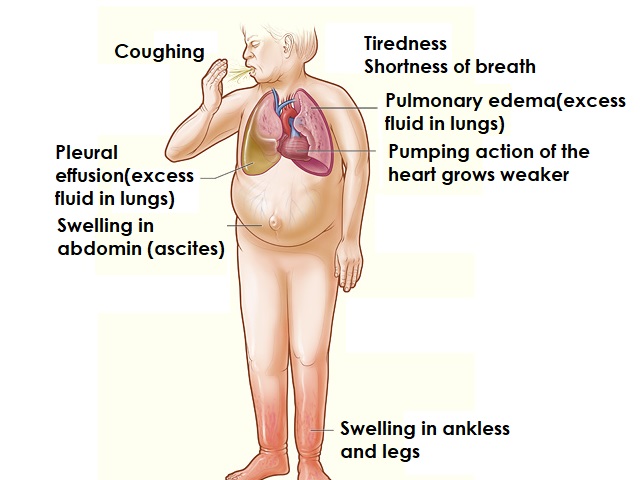
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Shortness of breath.
- Nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite.
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating.
- Itching and dry skin.
- Muscle cramps and twitches.
Causes of Kidney Failure:
Kidney failure can have various causes, including:
- Chronic kidney disease (CKD): Conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain kidney diseases can lead to gradual and irreversible kidney damage.
- Acute kidney injury (AKI): Sudden and severe kidney damage can occur due to factors like infections, dehydration, medications, and reduced blood flow to the kidneys.
- Kidney stones: Obstructive kidney stones can cause kidney damage if left untreated.
- Urinary tract blockages: Conditions that obstruct the normal flow of urine, such as an enlarged prostate or tumors, can lead to kidney failure.
Effects of Kidney Failure:
Kidney failure can have serious effects on the body, including:
- Fluid retention and electrolyte imbalances.
- Accumulation of waste products and toxins in the blood.
- Anemia and decreased production of red blood cells.
- Weakened immune system and increased susceptibility to infections.
- Cardiovascular complications, such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
- Bone disorders and mineral imbalances.
Treatment and Prevention of Kidney Failure:
The treatment options for kidney failure depend on the underlying cause and the stage of the condition. Treatment approaches may include:
- Medications: To control symptoms, manage complications, and slow down the progression of kidney damage.
- Dialysis: A process that filters waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys can no longer perform this function adequately.
- Kidney transplant: In cases of end-stage kidney failure, a transplant may be considered as a treatment option.
Prevention strategies for kidney failure include managing underlying conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding excessive use of certain medications, and staying hydrated.
It is important to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and guidance on prevention strategies for kidney failure.
References:
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2020). Kidney disease statistics for the United States. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-statistics/kidney-disease