6 Signs You May Have Renal Cell Carcinoma -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
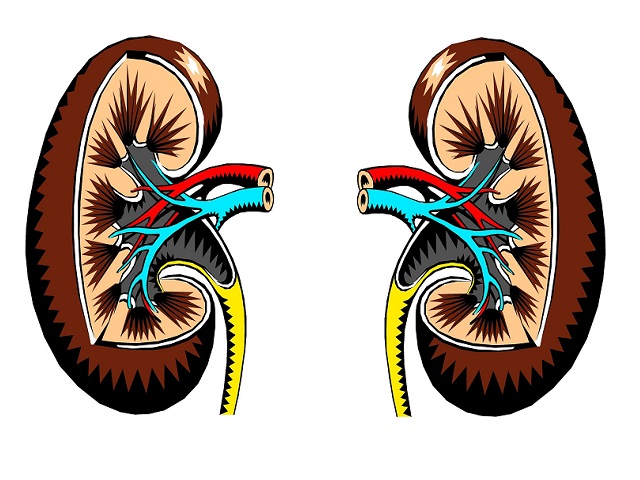
Renal cell carcinoma, also known as kidney cancer, is a malignant tumor that originates in the cells of the kidney. It is the most common type of kidney cancer in adults, accounting for approximately 90% of cases. Renal cell carcinoma typically arises from the tubular cells of the kidney, which play a crucial role in filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
Symptoms of Renal Cell Carcinoma:
Renal cell carcinoma may present with various symptoms. Common signs include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Lower back pain or pain in the side
- Unintentional weight loss
- Fatigue
- A mass or lump in the abdomen
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
Diagnosis of Renal Cell Carcinoma:
To diagnose renal cell carcinoma, several steps are involved. These include:
- Medical history and physical examination to assess symptoms and overall health
- Diagnostic imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the kidneys and detect abnormalities or tumors
- Biopsy, if necessary, to obtain a tissue sample for microscopic examination and confirmation of cancer cells
Causes of Renal Cell Carcinoma:
The development of renal cell carcinoma can be influenced by several factors, including:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- High blood pressure
- Family history of kidney cancer
- Genetic conditions such as von Hippel-Lindau disease
- Exposure to certain chemicals or substances like asbestos or cadmium
- Long-term dialysis treatment
Effects of Renal Cell Carcinoma:
Renal cell carcinoma can have various effects on the body. These include:
- Impaired kidney function, leading to decreased filtration and urine production
- Increased risk of blood clots or infections
- Bone involvement, causing bone pain or fractures
- Negative impact on overall health and quality of life
Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma:
Treatment options for renal cell carcinoma depend on factors such as the stage and extent of the cancer. Common approaches include:
- Surgery (partial or complete nephrectomy) to remove the tumor
- Targeted therapy using drugs that specifically target cancer cells
- Immunotherapy to stimulate the immune system against cancer cells
- Radiation therapy to destroy cancer cells with high-energy beams
- Participation in clinical trials or experimental treatments
Prevention of Renal Cell Carcinoma:
While complete prevention may not be possible, individuals can take steps to reduce their risk, such as:
- Avoiding or quitting smoking
- Maintaining a healthy body weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Managing high blood pressure effectively
- Minimizing exposure to harmful chemicals or substances
Note: It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management of renal cell carcinoma.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2022). Kidney Cancer (Adult) - Renal Cell Carcinoma. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kidney-cancer