6 Signs You May Have Type 2 Diabetes -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from insulin resistance and impaired insulin production. Unlike type 1 diabetes, in which the body does not produce insulin, individuals with type 2 diabetes still produce insulin, but their body does not effectively use it. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, sedentary behavior, and unhealthy eating habits.
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes:
The symptoms of type 2 diabetes may develop gradually and can include:
- Increased thirst and frequent urination.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing wounds.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet.
- Recurrent infections, such as urinary tract infections or yeast infections.
However, some individuals with type 2 diabetes may not experience any noticeable symptoms initially (American Diabetes Association, 2021a).
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The primary risk factors and causes of type 2 diabetes include:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly around the abdomen, increases the risk of developing insulin resistance.
- Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism.
- Unhealthy eating habits: Diets high in processed foods, sugary beverages, and saturated fats can contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes.
- Family history: Having a family history of type 2 diabetes increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Age: The risk of type 2 diabetes increases with age, particularly after the age of 45.
- Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Asians, have a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Although these factors increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, it is important to note that the disease can also occur in individuals without apparent risk factors (American Diabetes Association, 2021b).
Effects of Type 2 Diabetes:
If left uncontrolled, type 2 diabetes can lead to various complications and health effects, including:
- Cardiovascular complications: Type 2 diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, high blood pressure, and narrowing of blood vessels (atherosclerosis).
- Nerve damage (neuropathy): Chronic high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain, particularly in the hands and feet.
- Kidney damage (nephropathy): Diabetes can affect the kidneys' filtering function and lead to kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Eye problems (retinopathy): Uncontrolled diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and even blindness.
- Foot complications: Nerve damage and poor circulation can increase the risk of foot ulcers, infections, and, in severe cases, amputation.
- Increased risk of other conditions: Type 2 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of certain conditions, including obesity, sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, and certain types of cancer.
Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes:
The treatment of type 2 diabetes aims to manage blood sugar levels and prevent or manage complications. Treatment strategies may include:
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy eating plan, engaging in regular physical activity, and achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Oral medications: Medications that help lower blood sugar levels by various mechanisms, such as improving insulin sensitivity or reducing glucose production by the liver.
- Injectable medications: In some cases, injectable medications such as GLP-1 receptor agonists or insulin may be prescribed to control blood sugar levels.
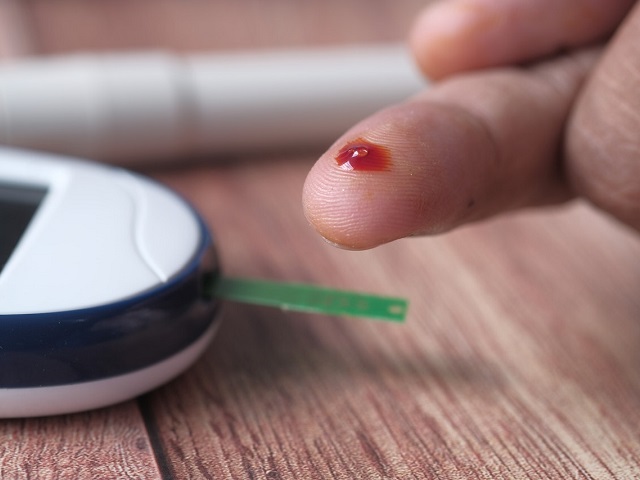
- Blood sugar monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels to track how food, physical activity, and medication affect glucose levels.
- Education and support: Learning about diabetes self-care, monitoring, and management techniques, and receiving support from healthcare professionals and diabetes educators.
Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes:
Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle modifications. Some preventive measures include:
- Healthy eating: Following a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and limited saturated fats and sugary foods.
- Regular physical activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, along with strength training exercises.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight or losing excess weight if overweight or obese.
- Regular check-ups: Undergoing regular check-ups with healthcare professionals to monitor blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and other related parameters.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance and recommendations (American Diabetes Association, 2021a).
References:
American Diabetes Association. (2021a). Type 2 diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/type-2