7 Signs You May Have Type 1 Diabetes -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Type 1 diabetes, also known as insulin-dependent diabetes or juvenile diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by the body's inability to produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to a deficiency of insulin. As a result, individuals with type 1 diabetes require lifelong insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes:
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes often develop rapidly and can include:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Increased hunger.
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Blurred vision.
- Irritability or mood changes.
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections.
These symptoms may be severe and require immediate medical attention. If left untreated, type 1 diabetes can lead to a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) (American Diabetes Association, 2021a).
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes:
The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is not fully understood. It is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some potential causes and risk factors include:
- Autoimmune response: Type 1 diabetes is considered an autoimmune disease, where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
- Genetic predisposition: Certain genetic factors can increase the risk of developing type 1 diabetes. Having a family member with the condition, especially a parent or sibling, increases the likelihood.
- Environmental triggers: Viral infections, such as enteroviruses or respiratory infections, may trigger the autoimmune response in individuals with a genetic predisposition.
More research is needed to fully understand the causes of type 1 diabetes�
Effects of Type 1 Diabetes:
If left unmanaged, type 1 diabetes can have significant effects on various aspects of an individual's health. These effects may include:
- High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia): Chronic high blood sugar can lead to complications affecting the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and cardiovascular system.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA): Without insulin, the body cannot use glucose for energy, and fat breakdown produces ketones, leading to the dangerous condition of DKA.
- Long-term complications: Uncontrolled type 1 diabetes can increase the risk of long-term complications, including heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), and eye problems (retinopathy).
Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes:
The primary treatment for type 1 diabetes is insulin therapy, which involves injecting insulin into the body. Other treatment approaches may include:
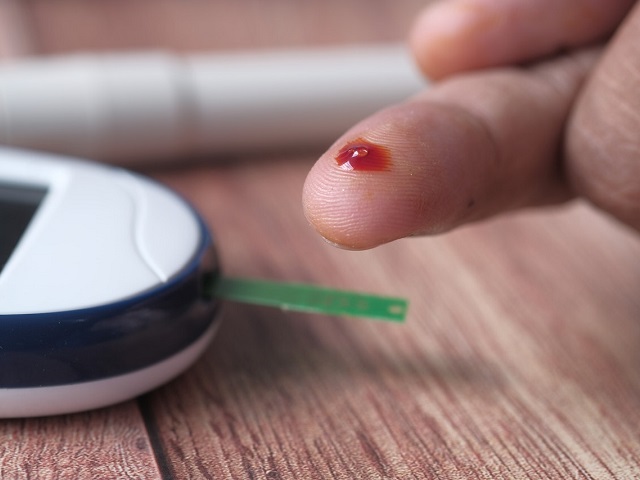
- Blood sugar monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels using a glucose meter to adjust insulin doses accordingly.
- Carbohydrate counting: Managing carbohydrate intake to match insulin doses.
- Healthy eating: Following a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and limited saturated fats and sugary foods.
- Physical activity: Engaging in regular exercise to help manage blood sugar levels and promote overall health.
- Education and support: Learning about diabetes management, self-care techniques, and receiving support from healthcare professionals and diabetes educators.
Prevention of Type 1 Diabetes:
Currently, there is no known way to prevent type 1 diabetes. However, ongoing research is being conducted to understand the disease better and develop potential preventive strategies.
References:
American Diabetes Association. (2021a). Type 1 diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.diabetes.org/diabetes/type-1