9 Signs You May Have Hepatitis B -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
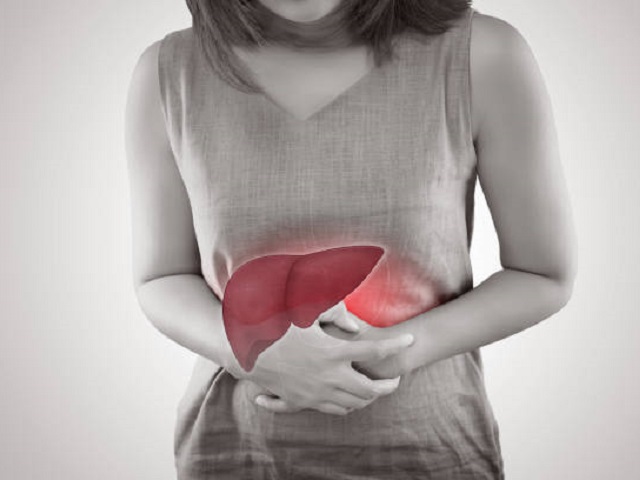
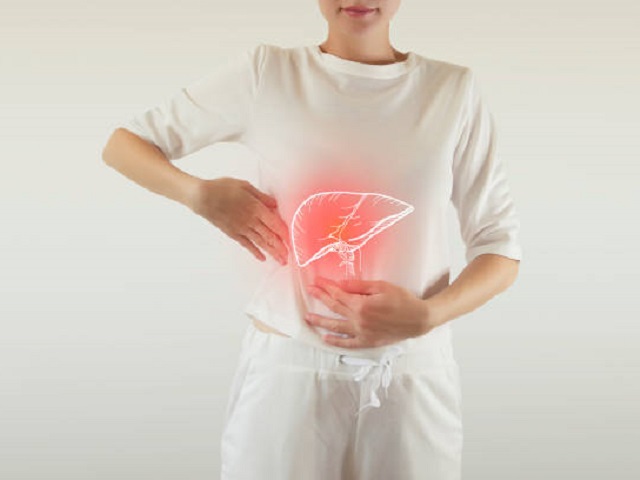
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver and is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). It can lead to both acute and chronic liver disease and poses a significant global health burden. The virus is transmitted through contact with infected blood or other body fluids, such as semen and vaginal fluids, as well as from mother to child during childbirth.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B:
The symptoms of hepatitis B can vary depending on the stage of the infection. Some individuals may not experience any symptoms, while others may develop the following:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Dark urine.
- Clay-colored stools.
- Joint pain.
- Fever.
These symptoms typically occur during the acute phase of the infection, which can last for several weeks. However, in some cases, hepatitis B may progress to a chronic infection, leading to long-term liver damage and complications (World Health Organization, 2021a).
Causes of Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus, which is primarily transmitted through:
- Direct contact with infected blood, such as through sharing contaminated needles or syringes, receiving unsafe medical procedures or blood transfusions, or needlestick injuries in healthcare settings.
- Unprotected sexual contact with an infected person.
- Mother-to-child transmission during childbirth.
The virus can survive outside the body for at least seven days, allowing it to spread through various means of transmission (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020).
Effects of Hepatitis B:
Hepatitis B can have significant effects on the liver and overall health. Potential complications and effects may include:
- Acute liver failure: In severe cases, acute hepatitis B can lead to liver failure, requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Chronic hepatitis: If the infection persists for more than six months, it is considered chronic hepatitis B, which can lead to liver cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), liver cancer, and other liver-related complications.
- Increased risk of liver cancer: Chronic hepatitis B infection significantly increases the risk of developing liver cancer.
- Transmission to others: People with chronic hepatitis B can unknowingly transmit the virus to others, including sexual partners and infants during childbirth.
Treatment and Prevention of Hepatitis B:
Treatment and prevention strategies for hepatitis B include:
- Antiviral medications: Antiviral drugs, such as interferon and oral antiviral agents, may be prescribed to manage chronic hepatitis B and reduce the risk of liver-related complications.
- Regular monitoring: People with chronic hepatitis B may require regular monitoring of liver function and viral load to assess disease progression and determine the need for treatment.
- Hepatitis B vaccination: Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent hepatitis B. The vaccine is recommended for all infants, children, and adults who have not been previously vaccinated.
- Safe practices: Practicing safe sex, avoiding sharing needles or other injection equipment, and using standard precautions in healthcare settings can help prevent hepatitis B transmission.
It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures for hepatitis B (World Health Organization, 2021b).
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Hepatitis B questions and answers for the public. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hbv/bfaq.htm
World Health Organization. (2021a). Hepatitis B. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b
World Health Organization. (2021b). Hepatitis B: Key facts. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b