9 Signs You May Have Hepatitis C -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
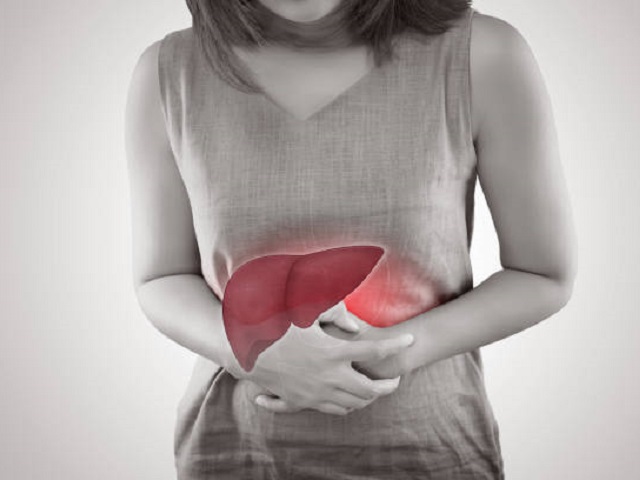
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver and is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It can lead to both acute and chronic liver disease and is a major global health concern. Hepatitis C is mainly transmitted through contact with infected blood, such as through sharing contaminated needles or other drug paraphernalia, receiving unsafe medical procedures, or blood transfusions before the implementation of stringent screening measures.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C:
Many individuals with hepatitis C may not experience any symptoms, particularly during the early stages of the infection. However, some common symptoms may include:
- Fatigue and weakness.
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes).
- Abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Loss of appetite.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Dark urine.
- Clay-colored stools.
- Joint pain.
- Fever.
These symptoms are not specific to hepatitis C and can be present in other liver-related conditions as well. Therefore, it is important to undergo proper testing for accurate diagnosis (World Health Organization, 2021a).
Causes of Hepatitis C:
Hepatitis C is caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), which is primarily transmitted through:
- Sharing contaminated needles or other equipment used for injecting drugs.
- Unsafe medical procedures, such as the use of inadequately sterilized medical equipment or the re-use of syringes and needles.
- Blood transfusions and organ transplants before the implementation of effective screening measures.
- Less commonly, hepatitis C can be transmitted through sexual contact and from mother to child during childbirth.
It is important to note that hepatitis C is not spread through casual contact, breastfeeding, or through food or water (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2021a).
Effects of Hepatitis C:
Hepatitis C can have various effects on the liver and overall health, including:
- Chronic hepatitis: Most individuals infected with hepatitis C develop a chronic infection that can lead to long-term liver inflammation.
- Liver cirrhosis: Chronic hepatitis C can progress to liver cirrhosis, which is characterized by the development of scar tissue in the liver. Cirrhosis can impair liver function and lead to complications.
- Liver cancer: Individuals with chronic hepatitis C are at an increased risk of developing liver cancer (hepatocellular carcinoma).
- Liver failure: In advanced cases, chronic hepatitis C can lead to liver failure, necessitating liver transplantation.
Treatment and Prevention of Hepatitis C:
Advancements in medical treatment have led to highly effective therapies for hepatitis C. The goals of treatment are to eliminate the virus, reduce liver inflammation, prevent liver-related complications, and improve overall health. Treatment options may include:
- Antiviral medications: Direct-acting antiviral drugs are the mainstay of treatment for hepatitis C. These medications target the virus and can cure the infection in the majority of cases.
- Regular monitoring: Individuals with chronic hepatitis C may require regular monitoring of liver function, viral load, and other parameters to assess disease progression and response to treatment.
- Prevention of transmission: Prevention strategies for hepatitis C include avoiding sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia, practicing safe sex, and ensuring the use of sterile medical equipment and safe blood transfusions (World Health Organization, 2021b).
It is important to consult with healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, treatment, and preventive measures for hepatitis C.
References:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2021a). Hepatitis C questions and answers for the public. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hcv/cfaq.htm
World Health Organization. (2021a). Hepatitis C. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c
World Health Organization. (2021b). Hepatitis C: Key facts. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c