4 Signs You May Have Uterine Cancer -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
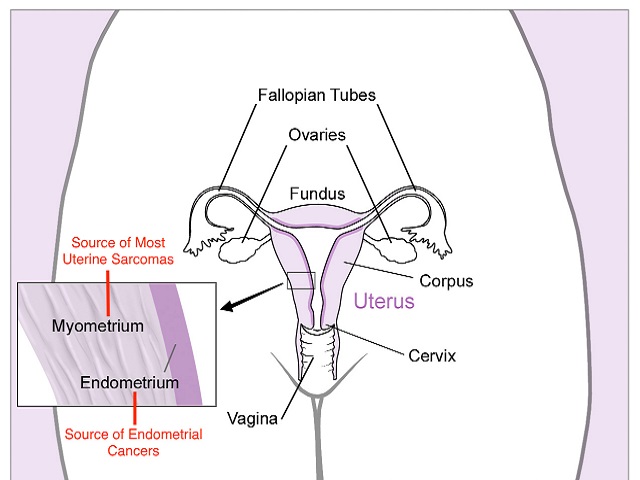
Uterine cancer, also known as endometrial cancer, is a type of cancer that develops in the uterus, specifically in the lining of the uterus called the endometrium. Uterine cancer primarily arises from the abnormal growth of cells in the endometrium, the inner lining of the uterus. It is the most common type of cancer affecting the female reproductive system. Here is an explanation of uterine cancer, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, causes, effects, treatment, and prevention:
Symptoms of Uterine Cancer:
The symptoms of uterine cancer can include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: Postmenopausal bleeding or irregular bleeding between menstrual cycles.
- Pelvic pain or discomfort: Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic area.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge: Unusual vaginal discharge, which may be watery or blood-tinged.
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits: Changes in bowel movements or urination patterns.
Diagnosis of Uterine Cancer:
Diagnosing uterine cancer involves several methods to evaluate and confirm the presence of cancer:
- Medical history and physical examination: A healthcare professional will inquire about symptoms and medical history, followed by a physical examination of the pelvis.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the uterus and help detect abnormalities.
- Endometrial biopsy: A tissue sample from the endometrium is collected for analysis to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
- Dilation and curettage (D&C): In some cases, a D&C procedure may be performed to obtain tissue samples for further evaluation.
Causes of Uterine Cancer:
The exact causes of uterine cancer are not fully understood, but certain factors may increase the risk:
- Hormonal imbalances: Changes in hormone levels, specifically an excess of estrogen relative to progesterone, can contribute to the development of uterine cancer.
- Age and menopause: The risk of uterine cancer increases with age, and postmenopausal women are at higher risk.
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of uterine cancer, possibly due to increased estrogen levels.
- Hormone therapy: Prolonged use of estrogen-only hormone replacement therapy (HRT) without progesterone can increase the risk.
Effects of Uterine Cancer:
If left untreated or undetected, uterine cancer can have significant effects on a person's health:
Spread to other organs: Uterine cancer can spread to nearby tissues and lymph nodes, as well as distant organs, leading to more advanced stages of the disease and reduced survival rates.
Treatment of Uterine Cancer:
The treatment of uterine cancer depends on factors such as the stage, grade, and overall health of the individual:
- Surgery: The main treatment for uterine cancer involves surgically removing the uterus (hysterectomy) and sometimes nearby lymph nodes.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy may be used before or after surgery to kill cancer cells or reduce the risk of recurrence.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be recommended in cases of advanced or recurrent uterine cancer.
- Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy, such as progesterone-based medications, may be used for certain types of uterine cancer.
Prevention of Uterine Cancer:
While it may not be possible to prevent uterine cancer entirely, certain measures may reduce the risk:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Staying within a healthy weight range and engaging in regular physical activity can help reduce the risk.
- Hormone therapy considerations: If considering hormone replacement therapy, it is important to discuss the risks and benefits with a healthcare professional.
- Regular check-ups: Routine gynecologic check-ups and screenings can help detect any abnormalities in the uterus at an early stage.
It is crucial for individuals to consult healthcare professionals for accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and prevention strategies related to uterine cancer.
Image Attribution:
Featured image by Crosscoupling, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons