6 Signs You May Have Penile Cancer -- Symptoms, Causes, Effects, Treatment and Prevention
Image by Laboratoires Servier, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
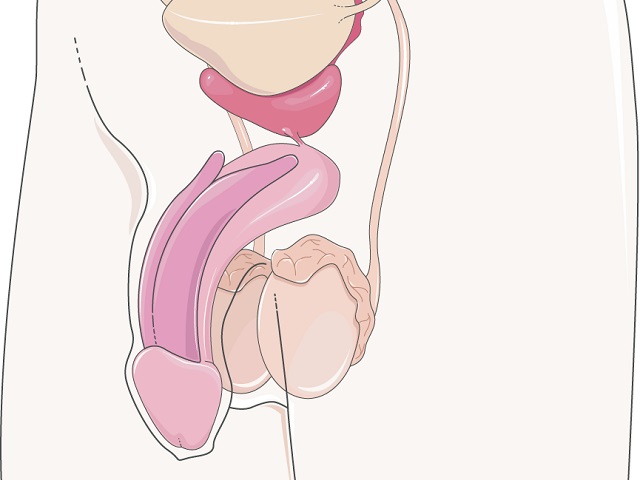
Penile cancer is a rare form of cancer that develops in the tissues of the penis. It typically starts in the skin cells and can spread to other parts of the organ. Penile cancer is more commonly diagnosed in older men and is often associated with poor hygiene and certain risk factors. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for favorable outcomes.
Symptoms of Penile Cancer:
The symptoms of penile cancer may include:
- Changes in the skin of the penis, such as discoloration, thickening, or ulceration
- Formation of a lump or growth on the penis
- Persistent sore or ulcer that does not heal
- Bleeding or discharge from the penis
- Changes in the appearance of the foreskin, such as tightening or phimosis
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin area
Diagnosis of Penile Cancer:
To diagnose penile cancer, healthcare professionals may employ various methods, including:
- Physical examination: A thorough examination of the penis and surrounding areas to check for any abnormalities.
- Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is collected from the affected area and analyzed under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
- Imaging tests: Imaging techniques like ultrasound, MRI, or CT scan may be used to determine the extent of the disease and evaluate lymph node involvement.
Causes of Penile Cancer:
Several factors can contribute to the development of penile cancer, including:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, particularly certain high-risk types
- Poor personal hygiene
- Phimosis (tight foreskin)
- Smoking
- Age, with the risk increasing with age
- History of genital warts or other sexually transmitted infections
Effects of Penile Cancer:
Penile cancer can have physical, emotional, and psychological effects on affected individuals. The specific effects may vary depending on the stage and treatment of the cancer. Possible effects can include:
- Disruption of sexual function and intimacy
- Impact on body image and self-esteem
- Psychological distress, including anxiety and depression
- Potential for recurrence or spread to nearby or distant organs
Treatment of Penile Cancer:
Treatment options for penile cancer depend on various factors, including the stage, location, and individual circumstances. Common treatment approaches may include:
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the cancerous tissue, such as a partial or total penectomy, lymph node dissection, or reconstructive surgery.
- Radiation therapy: High-energy radiation is used to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors.
- Chemotherapy: Medications are administered to destroy cancer cells or inhibit their growth.
- Immunotherapy: Drugs are used to boost the body's immune system to fight against cancer cells.
Prevention of Penile Cancer:
While the prevention of penile cancer is not guaranteed, some strategies that may help reduce the risk include:
- HPV vaccination: Getting vaccinated against the high-risk HPV types associated with penile cancer.
- Safe sexual practices: Practicing safe sex and using barrier methods to reduce the risk of HPV and other sexually transmitted infections.
- Good hygiene: Maintaining proper hygiene of the genital area, including regular washing and cleaning.
- Regular check-ups: Undergoing routine medical examinations and seeking prompt medical attention for any unusual symptoms.
Note: It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plan, and guidance on prevention strategies.
References:
American Cancer Society. (2022). Penile Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/cancer/penile-cancer.html
National Cancer Institute. (2022). Penile Cancer Treatment (PDQ) - Health Professional Version. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.gov/types/penile/hp/penile-treatment-pdq
Cancer Research UK. (2021). Penile Cancer. Retrieved from https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/penile-cancer